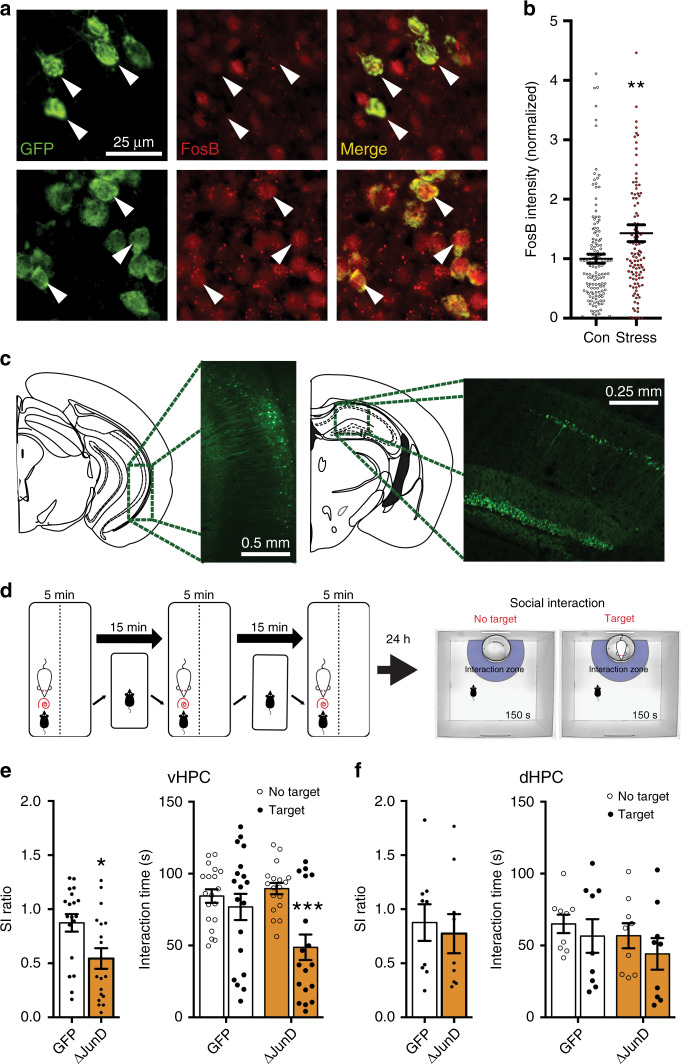
Fig. 1. ΔFosB expression in the ventral hippocampus is necessary for CSDS resilience.
a Representative images of vHPC CA1 coronal sections (×40) showing immunofluorescent labeling of NAc-projecting neurons expressing GFP (left), ΔFosB (red, middle) and merge (right). Stressed mice (bottom panels; n = 109 cells) show increased ΔFosB signal in GFP-positive cells compared to controls (top panels; n = 147 cells), as indicated by white arrows and quantified in (b). **P = 0.0048 (independent samples t-test compared to Control; 4 data points are outside the axis). c Representative figures and coronal sections showing viral-mediated GFP expression in ventral and dorsal HPC. d Experimental design for subthreshold defeat and social interaction (SI) test. e ΔJunD inhibition of ΔFosB in vHPC reduced SI ratio (left) and decreased investigation time of the social target (right). *P = 0.0125, ***P < 0.0001 (n = 19 GFP, n = 18 ΔJunD; SI ratio: independent samples t-test compared to GFP; investigation time: two-way mixed ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post-test GFP No Target vs Target). f ΔJunD expression in dHPC did not affect stress-induced social avoidance (n = 9 mice/group). All graphs are represented as mean ± SEM.