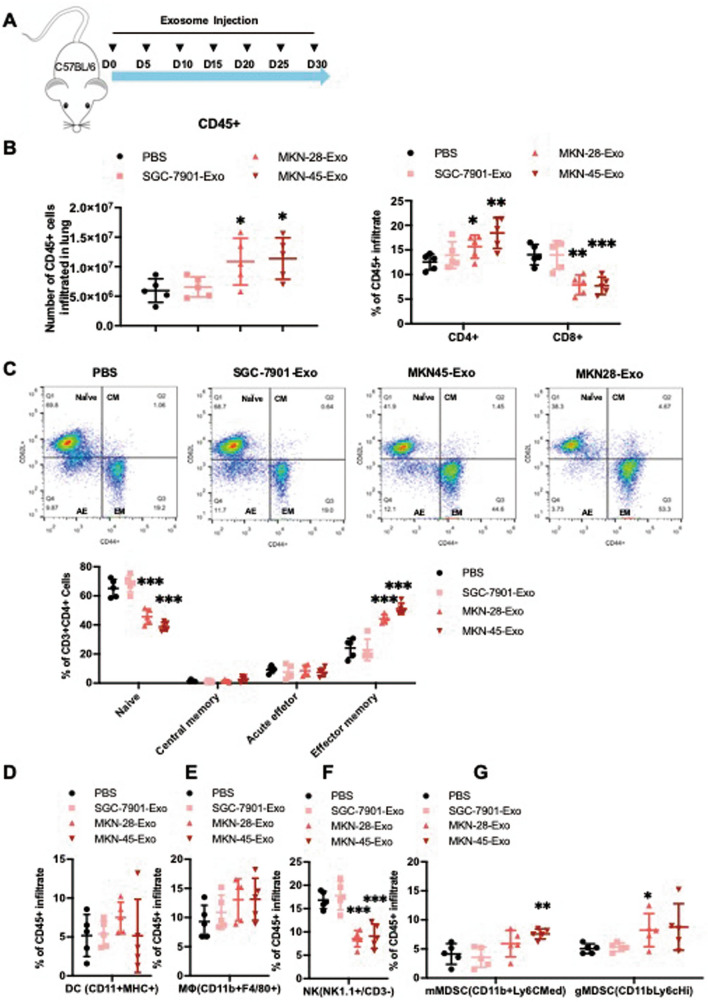
Figure 5.
Gastric cancer derived exosomes promote an immunosuppressive premetastatic niche formation in the lung. (A) Twenty C57BL/6 mice were divided into four groups. Mice in each group were injected with 20 μg SGC-7901, MKN-45, MKN-28 derived exosomes and PBS every 5 days, for a total of 30 days (tail intravenous). After 30 days, the organs were harvested, and the immune cells were obtained. Flow cytometry quantified the frequencies of immune subpopulations in the lungs of mice in each group. (B) Frequencies of subpopulations of CD4 (CD3+/CD4+) and CD8 T cells (CD3+/CD8+) subpopulations. (C) Representative frequencies of subpopulations of (naïve (CD44low/CD62Lhigh), central memory (CM, CD44high/CD62Lhigh), effector memory (EM, CD44high/CD62Llow), and acute effector CD4+T cells (AE, CD44low/CD62Llow) in the lung. (D–G) Representative frequency of DCs (CD11C+/MHCII+, D). Macrophages (Mø, CD11b+/F4/80+, E), NK (NK1.1+/CD3−, F) and MDSCs (gMDSCs, CD11b + /Ly6Cmed, mMDSCs CD11b+/Ly6Chigh, G), respectively. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5 animals/group) and analyzed by two-tailed Mann–Whitney U tests, *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001.