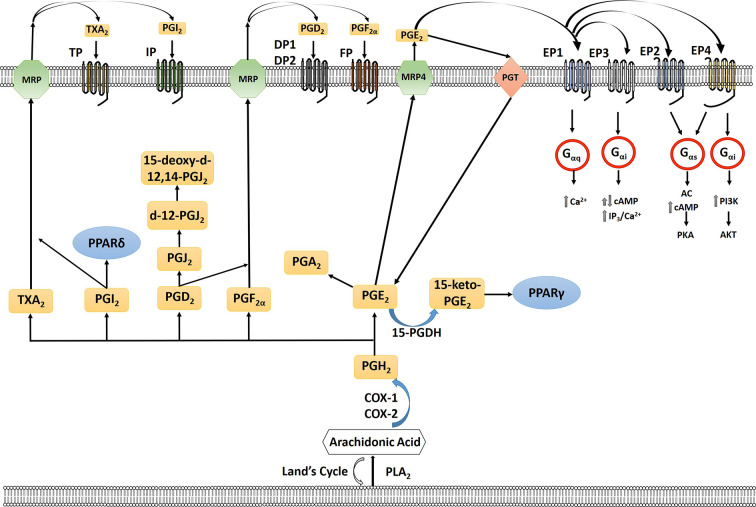
Figure 1.
Arachidonic acid (AA) is liberated from the plasma membrane via phospholipase A2 (PLA2). AA can be recycled by the Lands cycle, which is a reacylation/deacylation cycle, that serves to keep the concentration of free AA at a low level. AA is converted by cyclooxygenase 1 or 2 (COX-1/COX-2) to PGH2 which is then converted to PGE2, PGF2α, PGD2, PGI2, or TXA2 by prostaglandin specific synthases. PGE2 is exported out of the cell by multidrug resistance-associated protein four (MRP4) where it can bind to its receptors, the E series of prostaglandin receptors on the plasma membrane, EP1-4. Each of the G-protein-coupled- receptors signal through a different intracellular pathway: EP1 leads to elevation of intracellular calcium through Gαq, EP3, which exists in multiple isoforms, can lead to different responses with the majority acting to inhibit cAMP through Gαi as well as an increase in IP3/intracellular calcium; EP2 and EP4 cause stimulation of cyclic AMP (cAMP) production and protein kinase A (PKA) by sequential activation of Gαs and adenylate cyclase (AC); EP4 can also activate phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) through Gαi. PGE2 is imported back into the cell through prostaglandin transporter (PGT) where it can either be re-exported or inactivated by 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) to 15-keto-PGE2. 15-keto-PGE2 can signal through PPARγ. PGE2 can be converted to PGA2 through a dehydration reaction. PGD2 through a series of dehydrogenation reactions creates PGJ2, delta-12-prostaglandin J2 (d-12-PGJ2) and 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15-d-PGJ2). PGI2 can either signal through PPARδ intracellularly or exported via multidrug resistance protein (MRP) to signal through the IP receptor. TXA2 is exported out of the cell via MRP to signal through the TP receptor. PGF2α is exported out of the cell via MRP where it can signal via the FP receptor on the cell surface.