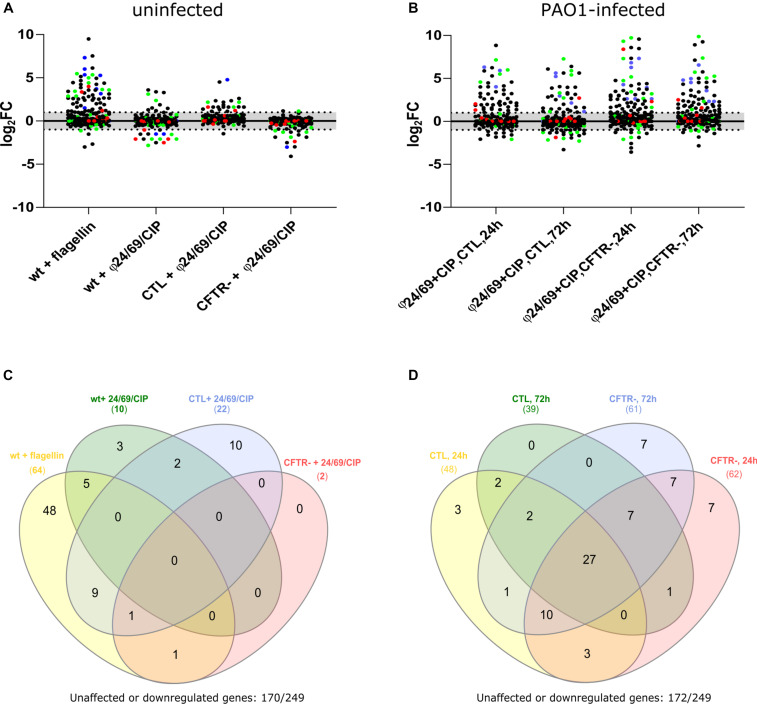
FIGURE 7.
Effect of phage cocktail, ciprofloxacin (CIP) and PAO1 infection on pro-inflammatory gene expression in wild type, CTL and cftr-cell lines (A) Cells were exposed to flagellin (positive control), as well as phage cocktail/CIP combinations for 18 h. At that point total RNA was extracted from the cells on the filter, and submitted to nanoString analysis. Flagellin served as the positive control and showed induction of 64/249 genes of the nCounter Inflammation Panel. Phage cocktail in combination with CIP showed induction of only a limited number of genes by the three cell lines (B) Infection of cells and subsequent treatment with phage cocktail/CIP showed induction of 39–61 genes among the CTL and cftr- cell lines, (C) Venn Diagram showing upregulated genes 24 h post-treatment in the absence of PAO1. The positive control flagellin showed specific induction of 48/249 genes. None of these 64 genes was up-regulated in the three cell lines by the presence of phage cocktail/CIP. (D) Venn Diagram showing upregulated genes after 24 and 72 h treatments of PAO1 infected CTL and cftr-cell lines. cftr-cells showed a broader pro-inflammatory response (induction of 61 (24 h) and 62 (72 h) genes), compared to the CTL cell line (induction of 39 (24 h) and 48 (72 h) genes) in the presence of PAO1 treated with phage cocktail and CIP.