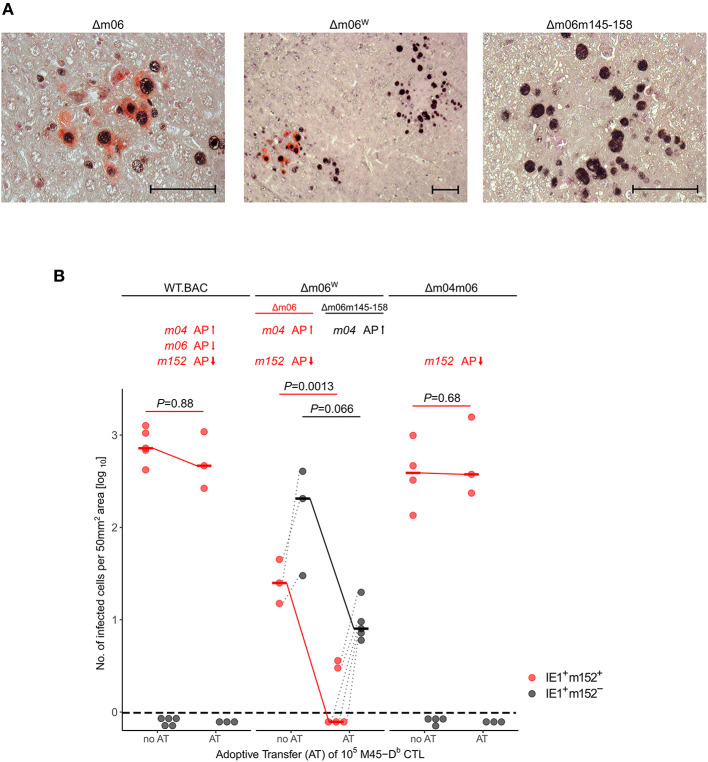
Figure 4.
2C-IHC analysis of liver infection. Reanalysis of stored liver specimens from a previously performed experiment [lung virus titers shown in Holtappels et al. (2006), Figure 8A]. C57BL/6 mice were immunocompromised by γ-irradiation (7.5 Gy) and infected at one footpad. Liver tissue sections were taken on day 12 after infection. (A) Virus spread in liver tissue. Infection was performed with 105 PFU of mCMV-Δm06W, now identified to represent a mixture of correct virus mCMV-Δm06 and a “large deletion” mutant mCMV-Δm06m145-158 that includes deletion of the m152 gene. 2C-IHC was performed to detect cytoplasmic m152 protein (red staining) specific for mCMV-Δm06 and intranuclear IE1 protein (black staining) expressed by both viruses. (Center panel) overview image showing foci of infection for both viruses in the mixture representing mCMV-Δm06W. (Left panel) detail image of cells infected with mCMV-Δm06 identified by red cytoplasmic staining of m152. (Right panel) Detail image of cells infected with mCMV-Δm06m145-158 characterized by absence of red cytoplasmic staining. Counterstaining was performed with hematoxylin. Bar markers: 50 μm. (B) vRAP expression-dependent control of liver tissue infection with the indicated viruses on day 12 after adoptive transfer of 105 antiviral CD8 T cells specific for the viral epitope M45-Db. 2C-IHC was performed to identify infected cells expressing m152 (red symbols) or lacking m152 (black symbols). (no AT) no adoptive transfer. (AT) adoptive transfer. Symbols represent mice tested individually. Data represent counts of infected liver cells in representative 50 mm2 tissue section areas. For further explanation, see the legend to Figure 3.