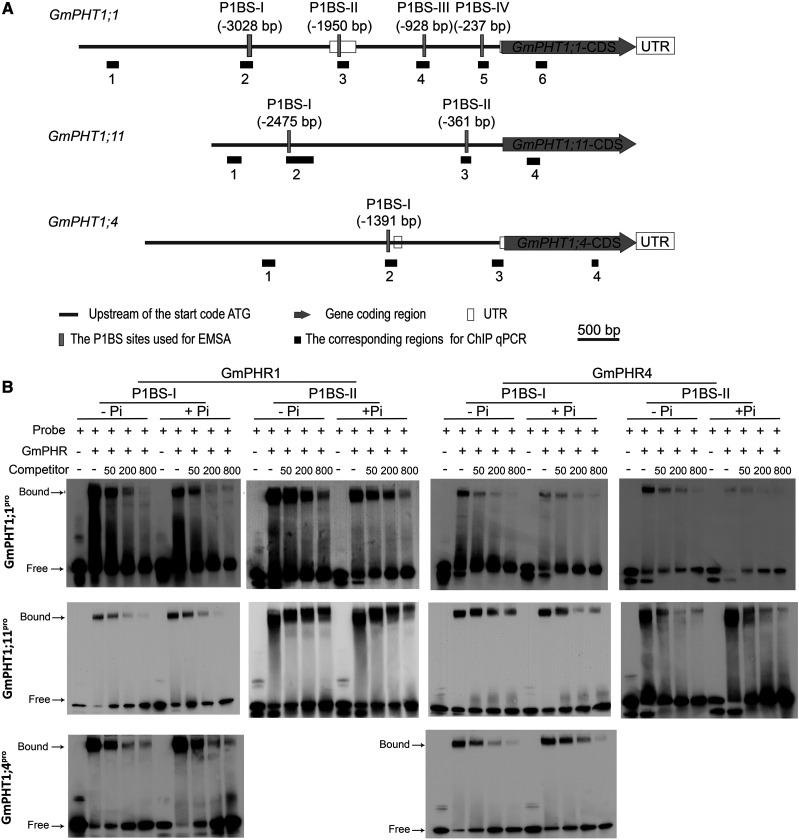
Figure 4.
GmPHR1 and GmPHR4 proteins bind directly to P1BS cis-elements in the promoters of GmPHT1 in vitro. A, Schematic structures of genomic genes GmPHT1;1, GmPHT1;11, and GmPHT1;4. The positions of the P1BS sites are indicated in parentheses (upstream of the start codon ATG), vertical gray bars represent the corresponding fragments for EMSA experiments (in B), and horizontal black bars display the corresponding regions for ChIP-qPCR detection (in Fig. 6). Gray bars represent the region upstream of the start codon ATG, gray arrow bars represent the gene-coding region, empty bars represent untranslated regions (UTR), vertical gray bars represent the PIBS sites used for EMSA, and black boxes represent the corresponding sites for ChIP qPCR in Figure 6. Scale bars (500 bp) are indicated above the genes. B, EMSA tests show that both GmPHR1 and GmPHR4 proteins bind to P1BS-containing fragments of GmPHT1;1 (top row), GmPHT1;11 (middle row), and GmPHT1;4 (bottom row) promoters independent of Pi concentration (+P, 1 mm KH2PO4; −P, 1 mm KCl in EMSA buffer). The fragments of P1BS-I and P1BS-II are indicated in A. Probe indicates labeled P1BS-containing fragments, while Competitor represents unlabeled P1BS-containing fragments. Numbers indicate fold of the concentration of Competitor compared with Probe. All experiments were performed with at least three biological repeats, which showed similar results. A single representative result is shown.