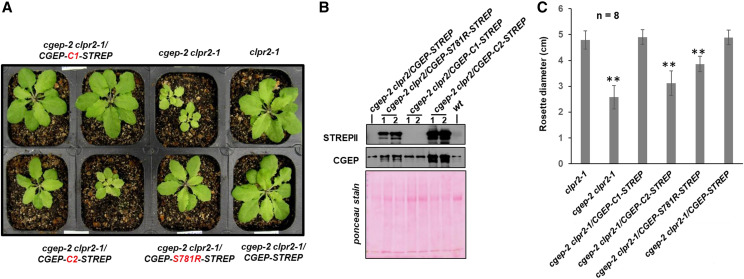
Figure 11.
Complementation and phenotyping of cgep-2 clpr2-1 expressing different CCEP variants. A, Visible phenotypes of clpr2-1, cgep-2 clpr2-1, and transgenic cgep-2 clpr2-1 plants complemented with 35S-CGEP-STREPII and CGEP-STREP variants. Plant were grown for 26 d on soil under a 16-h light/8-h dark cycle at 100-μmol photons m−2 s−1. Additional images of all genotypes are shown in Supplemental Figure S9. B, Detection of transgenic CGEP protein and the CGEP C-termini by STREPII and CGEP antisera in wild-type and complemented cgep-2 clpr2-1 plants by immunoblotting using soluble leaf extracts. Whereas there are high levels of CGEP protein detected, the STREPII-tagged portion is not detected in cgep-2 clpr2-1/CGEP-STREPII and cgep-2/CGEP-C1-STREPII, demonstrating autocatalytic cleavage of the C-termini in these CGEP variants. By contrast, detection of STREPII in cgep-2/CGEP-C1-STREPII demonstrates that C-terminal cleavage is inhibited. The Ponceau stains show the blot before immunodetection. C, Rosette diameter of clpr2-1, cgep-2, and cgep-2 clpr2-1 complemented with 35S-CGEP-STREPII and its modified forms S781R, C1, and C2. Plants were grown for 26 d on soil under a 16-h light/8-h dark cycle. Averages and sds are indicated for eight plants per genotype (n = 8). Asterisks indicate a significant difference (**P < 0.01) between the indicated genotype and cgep-2.