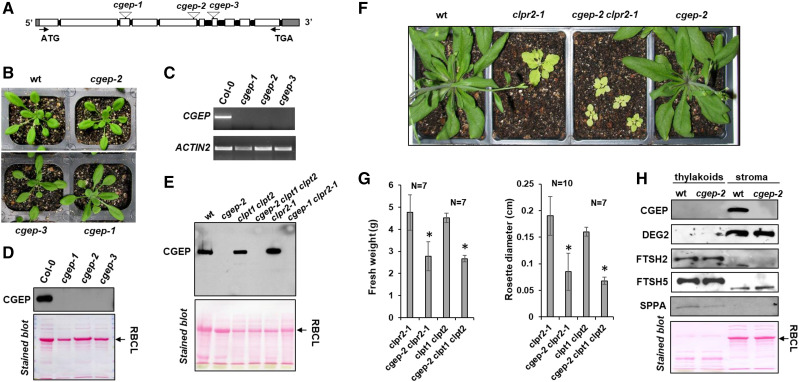
Figure 2.
Characterization of Arabidopsis T-DNA mutants and their visible phenotypes. A, Gene model structure and positions of the CGEP T-DNA insertion–mutant lines, assigned as cgep-1, cgep-2, and cgep-3. Introns are shown in black and the 5′-and 3′UTR in gray. Primers used for genotyping and RT-PCR are listed in Supplemental Table S4. B, Homozygous cgep alleles and wild type (wt) were grown on soil under a 18-h light/6-h dark regime with 130-μmol photons m−2 s−1 at 22°C. No obvious visible phenotypes were detected. Images of additional phenotyping on agar plants with and without the translational inhibitor CAP and soil grown under various abiotic stress conditions are shown in Supplemental Figure S2. C, mRNA levels of CGEP in wild-type and homozygous cgep-1, cgep-2, and cgep-3 as determined by RT-PCR. ACTIN2 was used as control. D, SDS-PAGE and immunoblot with anti-CGEP serum of total soluble leaf extracts shows that the three independent cgep lines completely lack accumulation of CGEP. Ponceau-stained blot is shown below. E, CGEP genetically interacts with Clp protease complex, as shown by visible growth and developmental phenotypes of the cgep clpr2-1 double mutant. F, SDS-PAGE and immunoblot with anti-CGEP serum of leaf extracts shows that the three cgep alleles completely lack accumulation of CGEP. Ponceau-stained blot before immunodetection is shown below. G, Quantitative measurement of fresh weight and rosette diameter in single (clpr2-1), double (cgep-2 clpr2-1; clpt1 clpt2), and triple (cgep-2 clpt1 clpt2) mutants. Asterisks indicate statistical significance using a t test (*P < 0.05). Additional images of mutants are shown in Supplemental Figure S3. H, Accumulation of thylakoid proteases SPPA, FTSH2, and FTSH5, and stromal DEG2 and CGEP, in wild type and cgep-2. This shows that the accumulation levels of these thylakoid proteases and DEG2 are unchanged cgep-2.