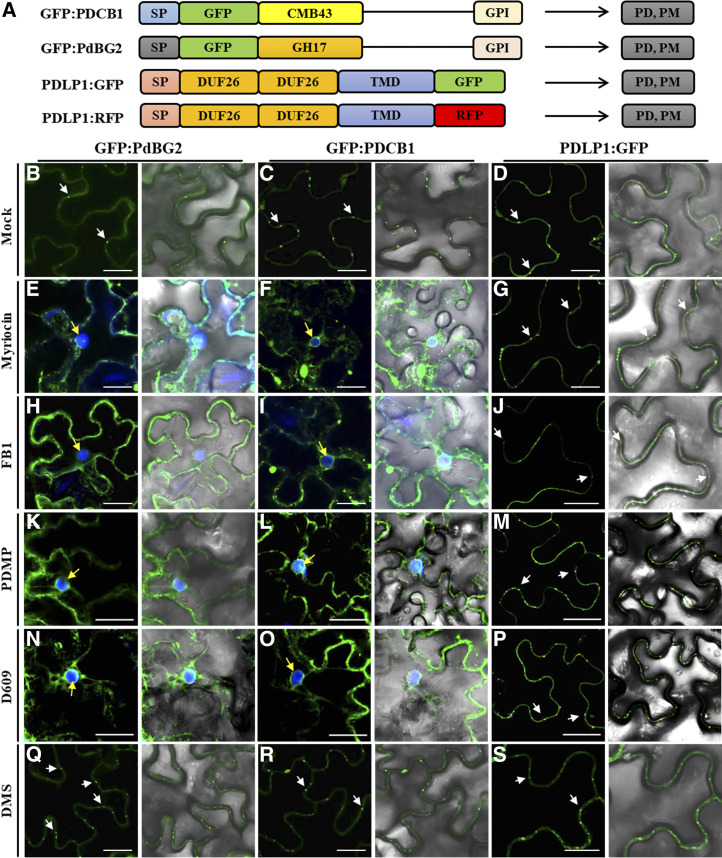
Figure 3.
GPI-anchored PD proteins are mislocalized in the presence of SL inhibitors. A, Structural organization of GFP:PDCB1, GFP:PdBG2, and PDLP1:GFP. Chimeric constructs consist of the signal peptides (SP) of PDCB1 and PdBG2, followed by the coding sequence of GFP fused to the callose-binding domain (CBM-43) for PDCB1, GH17 for PdBG2, and C-terminal GPI anchor signals. For PDLP1, the chimeric construct consists of the signal peptide of PDLP1, followed by double DUF26 domain, single transmembrane domain (TMD), and the coding sequence of GFP. B to S, Confocal images of leaf epidermal cells of N. benthamiana expressing fluorescent fusion proteins of PdBG2, PDCB1, and PDLP1 after SL inhibitor treatment, as follows: mock (B–D), 0.1 μm myriocin (E–G), 5 μm FB1 (H–J), 50 μm PDMP (K–M), 40 μm D609 (N–P), and 30 μm DMS (Q–S). PD localization is indicated by white arrows. 4′,6-Diamino-phenylindole (DAPI) staining was used to determine nuclear localization (yellow arrows). Bars = 10 μm.