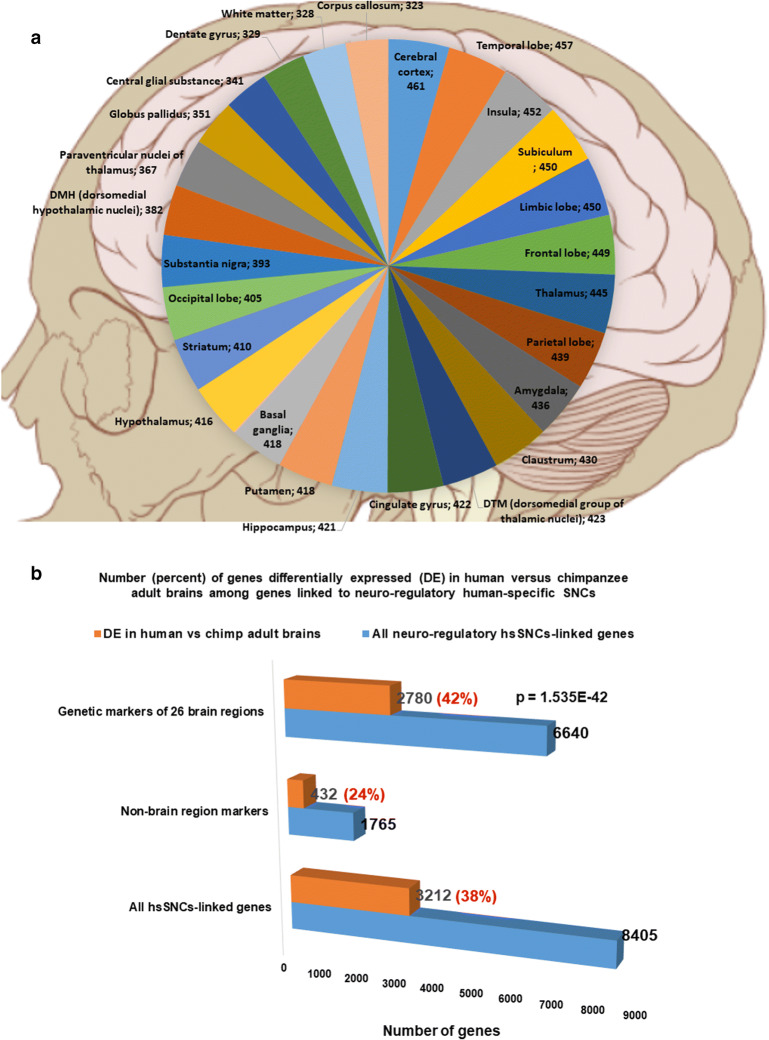
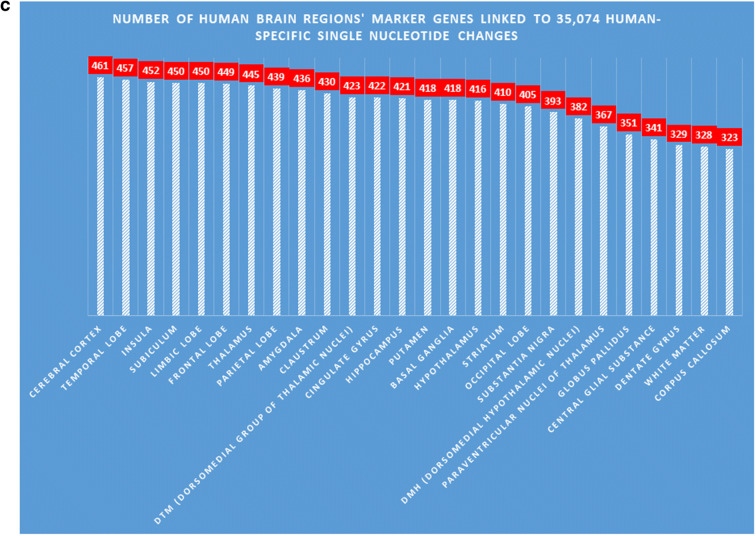
Fig. 2.
A dominant majority (6640 of 8405 genes; 79%) of genes linked to 35,074 human-specific single nucleotide changes (hsSNCs) in chromatin’s differentially accessible (DA) regions during human and chimpanzee brain development in cerebral organoids represents genetic markers of 26 human brain regions. a Number of brain regions’ marker genes linked to 35,074 neuro-regulatory hsSNCs in specified human brain regions (the normalized values calculated per 1000 region-specific marker genes are shown). Genes linked to hsSNCs were identified among genes significantly upregulated in specified human brain regions using the Allen Brain Atlas database (records manifesting increased expression at 1.5-fold cutoff were identified and selected for analyses). b Number (percent) of genes differentially expressed (DE) in human versus chimpanzee adult brains among genes linked to neuro-regulatory human-specific SNCs. Genes linked to hsSNCs were identified among genes differentially expressed in eight regions of human versus chimpanzee adult brains (Xu et al., 2018). c The relative ranking of the 26 brain regions based on the numbers of hsSNC-linked marker genes identified in each region of the human brain (normalized values per 1000 marker genes are reported)