Fig. 1. R-VECs self-assemble into 3D durable vessels in vitro and in vivo.
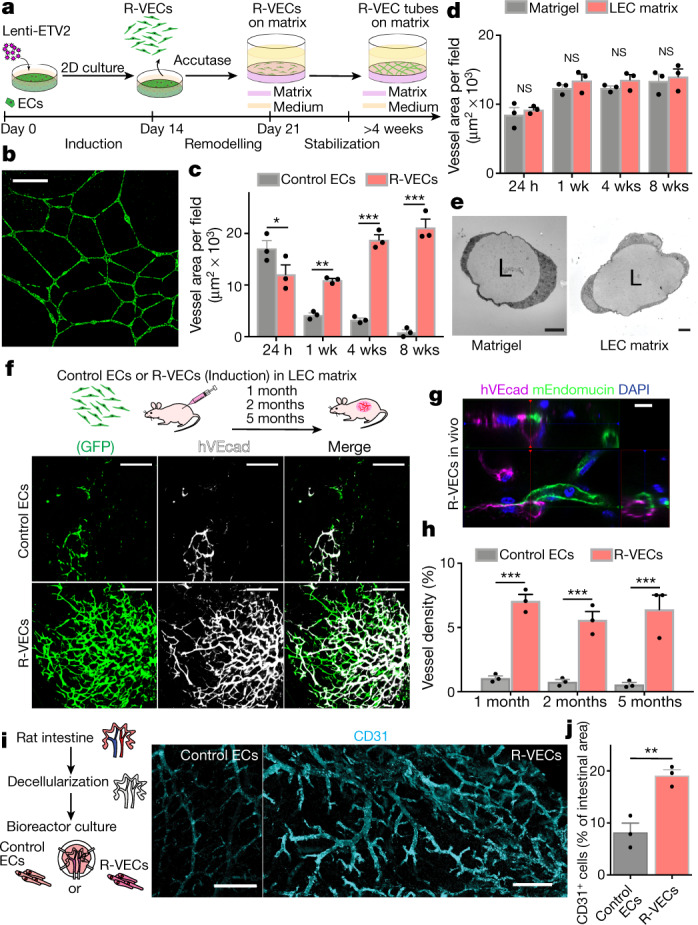
a, Experimental set-up for vessel formation. A total of 105 control ECs or R-VECs were plated on Matrigel in serum-free StemSpan tube-formation medium (Supplementary Data 2). Lenti-EVT2, lentiviral ETV2 expression construct. b, Z-stack of GFP+ R-VEC vessels at week 16. Scale bar, 1,000 μm. c, Quantification of tube formation in control ECs (HUVECs) and R-VECs (HUVEC-ETV2). d, Quantification of R-VEC vessels on Matrigel or LEC matrix. e, Electron microscopy images of stage-3 vessels on Matrigel and LEC matrix. L, lumen. Scale bars, 5 μm. f, Top, schematic of in vivo plug experiment in which control ECs or R-VECs fluorescently labelled with GFP were subcutaneously injected as a single-cell LEC suspension into SCID-beige mice. Bottom, whole-mount confocal images of R-VEC plugs and control EC plugs at five months. A fluorescently labelled antibody against human VEcadherin (hVEcad) was injected retro-orbitally before mice were euthanized. Scale bars, 200 μm. g, Orthogonal projection showing the anastomosis of mouse vessels and human VEcad+ vessels. Sections were post-stained for mouse endomucin (mEndomucin). Scale bar, 10 μm. h, Quantification of the density of human vessels in the plugs, defined as the percentage of GFP positive vessels of the scanned area. i, j, Experimental procedure for the decellularized intestine cultures (i, left). R-VECs repopulated the vasculature, lining blood vessels including the distal capillaries. At day 7 the bioreactors were stained for human CD31, imaged (i, right) and quantified (j). Scale bars, 500 μm. Data are mean ± s.e.m. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. For statistics, see Supplementary Data 1.
