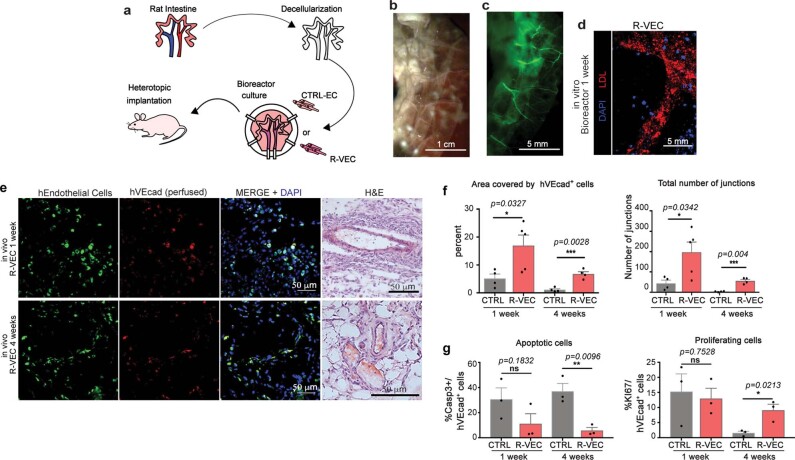
Extended Data Fig. 5. Decellularized intestinal scaffolds re-endothelialized with R-VECs engraft in vivo after omental implantation.
a, Schematic of experimental procedure for heterotopic implantation of decellularized intestinal scaffold vascularized using R-VECs. b, Rat intestines were cannulated through lumen, mesenteric artery and mesenteric vein. c, Decellularized intestine preserves native vasculature (green = GFP+ R-VECs). d, Seeded GFP labelled R-VECs spread evenly and reach distal capillaries. e, Heterotopic implantation of re-endothelialized intestines in immunodeficient mice omentum shows engraftment after 1 and 4 weeks of GFP+ R-VECs and anastomosis to the host vasculature as indicated by intravital intravenous injection of anti-human VEcad antibody (hVEcad). Representative H&E stainings show anatomical normal perfused vessels. f, Quantification of the area covered by R-VEC compared to CTRL-EC in implanted re-endothelialized intestines at 1 week and 4 weeks. g, Quantification of R-VEC and CTRL-EC proliferation and apoptosis in implanted re-endothelialized intestines at 1 and 4 weeks. Data are mean ± s.e.m. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. For statistics, see Supplementary Data 1.