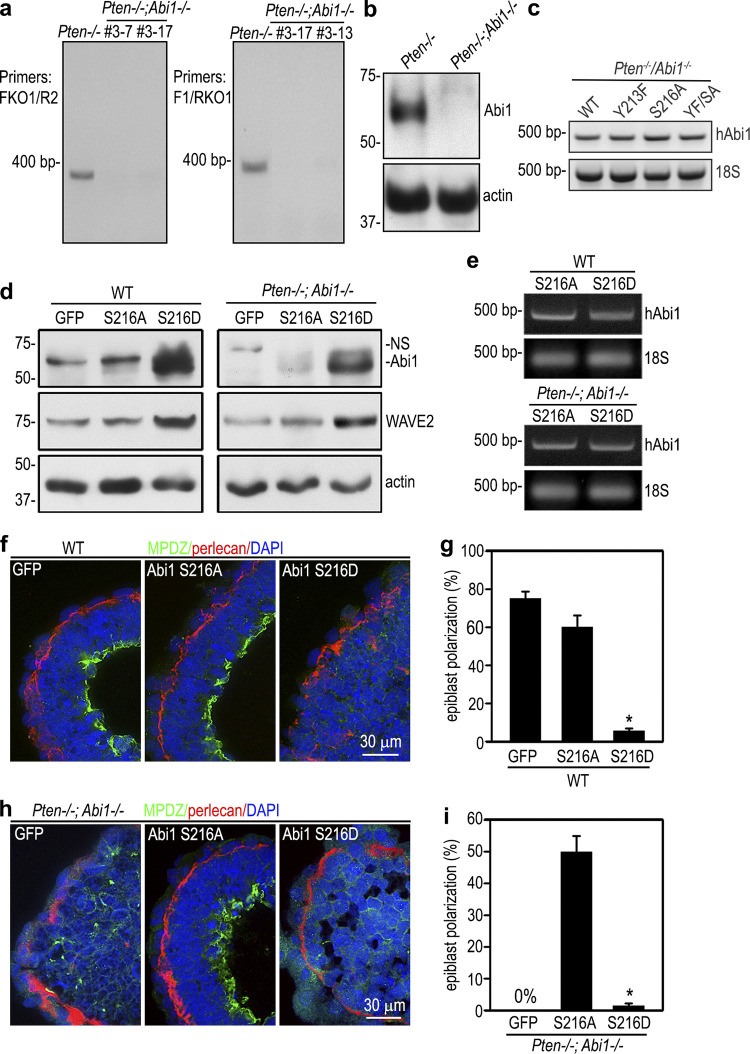
Figure S4.
Pten/Abi1 double-knockout EBs. (a) PCR genotyping was performed with two sets of primers spanning the sgRNA targeting site using DNA extracted from 5-d Pten−/− and Pten−/−;Abi1−/− EBs (clones 3-7, 3-17, and 3-13). FKO1, forward knockout primer 1; R2, reverse primer 2; F1, forward primer 1; RKO1, reverve knockout primer 1. (b) Immunoblots show loss of Abi1 expression in 5-d Pten−/−;Abi1−/− EBs (clone 3-13). (c) RT-PCR analysis of 5-d Pten−/−;Abi1−/− EBs stably transfected with wild-type (WT) human Abi1 (hAbi1) and the mutants Y213F, S216A, and Y213F/S216A (YF/SA) all showed similar expression levels of human Abi1 mRNAs. (d) Wild-type and Pten−/−;Abi1−/− EBs stably transfected with Abi1 S216A, S216D, or GFP were cultured for 5 d and analyzed by immunoblotting. Actin served as a loading control. (e) The mRNA level of transfected human Abi1 (hAbi1) in 5-d EBs were analyzed by RT-PCR. 18S RNA served as an internal control. (f and g) 5-d wild-type EBs stably transfected with Abi1 S216A, S216D, or GFP were stained for MPDZ. Basement membrane was stained for perlecan. The formation of a polarized epiblast layer was quantified by live phase-contrast microscopy and plotted as a percentage of total EBs examined. n = 651–707 for each group. Mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05 S216D versus S216A. (h and i) 5-d Pten−/−;Abi1−/− EBs stably transfected with Abi1 S216A, S216D, or GFP were stained for MPDZ. Basement membrane was stained for perlecan. Epiblast polarization was quantified and plotted as a percentage of total EBs examined. Mean ± SD. *, P < 0.01 versus the S216A group. n = 544–590 for each group.