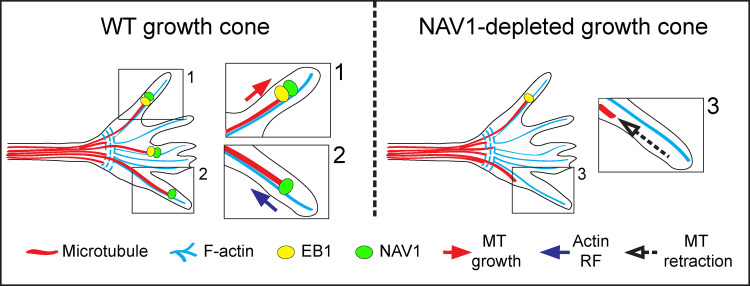
Figure 8.
Proposed model depicting how NAV1 affects GC dynamics. (1) In WT GCs, F-actin-bound NAV1 is recruited by EB1 on polymerizing MTs invading the GC periphery. (2) Once the EB complex disassembles and the MT stops growing, NAV1 remains at the nonpolymerizing MT plus ends by binding MTs directly. NAV1 bridges F-actin and nongrowing MTs, which either pause or are subjected to the F-actin RF. This NAV1-mediated crosslink prevents the exit of MT plus ends from the actin network. (3) NAV1 depletion reduces the number of nonpolymerizing MTs crosslinked to F-actin, resulting in their premature exit from the F-actin–rich area. We hypothesize that the ability of NAV1 to promote the persistence of MTs and their asymmetric capture by the F-actin network in the GC periphery is determinant to control GC dynamics and steering in response to guidance cues.