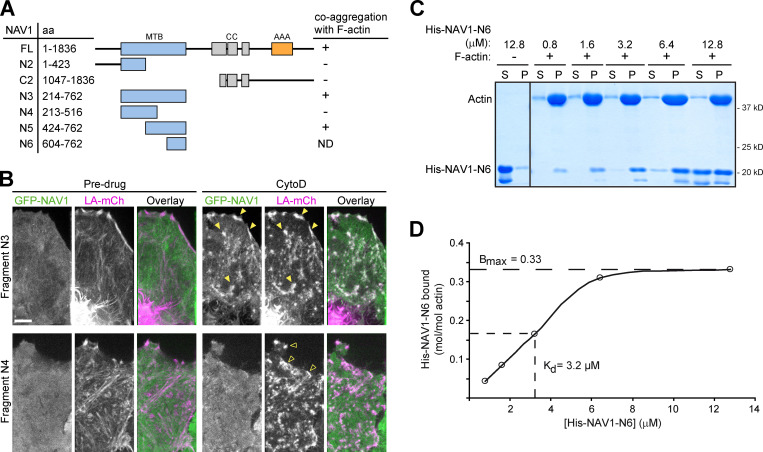
Figure S4.
NAV1 binds F-actin. Related to Fig. 3. (A) Schematic representation of the full-length and truncated forms of GFP-NAV1 constructs used in B. AAA+, predicted ATPase domain; CC, coiled coil; MTB, predicted microtubule-binding domain. (B) Fluorescence microscopy images of HeLa cells transfected with Lifeact-mCherry and the indicated GFP-NAV1 constructs and either left untreated or treated with cytochalasin D for 1 min. In control cells, GFP-NAV1-N3 and N4 appear soluble in the cytosol. GFP-NAV1-N3 relocalizes to Lifeact-positive aggregates of F-actin upon cytochalasin D treatment (closed arrowheads), whereas GFP-NAV1-N4 remains soluble (open arrowheads). Scale bar, 5 µm. (C) Coomassie-stained gel of the soluble (S) and pellet (P) fractions of an in vitro F-actin cosedimentation assay with purified His-tagged NAV1-N6 fragment (aa 604–762). (D) Saturation binding curve for His-NAV1-N6 and equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) calculated as described in Materials and methods.