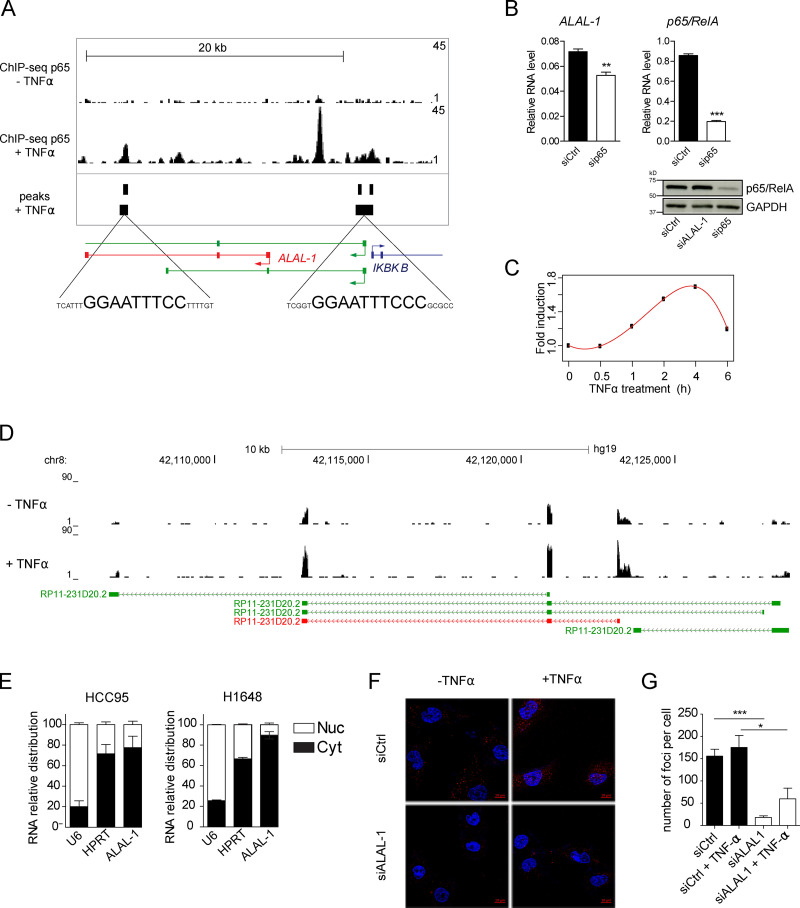
Figure 4.
ALAL-1 is a transcriptional target of NF-κB. (A) ChIP-seq signal of p65 in the ALAL-1 locus in HUVEC cells treated or not with TNFα. Peaks called in p65 ChIP-seq analysis in the A549 cell line and the consensus sequences corresponding to p65 binding sites are indicated below. In green, annotated ALAL-1 isoforms. (B) ALAL-1 RNA levels and p65 protein levels determined in HCC95 cells after p65 knockdown. Graphs of mean (± SEM) for three independent experiments are shown. Significance was determined by two-tailed unpaired t test and represented as **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. (C) Time course experiment showing the induction of ALAL-1 in HCC95 cells treated with TNFα. (D) RNA-seq tracks of ALAL-1 locus of HCC95 cells untreated or treated with TNFα for 4 h. In green, ALAL-1 annotated isoforms; in red, ALAL-1 isoform identified and studied. (E) Subcellular localization of ALAL-1 assessed by cell fractionation in the indicated cell lines. (F) RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization in HCC95 cells untreated and treated with TNFα. (G) Number of fluorescent foci detected by RNA FISH in cells transfected with control siRNA (siCtrl) or ALAL-1 siRNA (siALAL-1). At least 100 cells per condition were counted. Graph of mean (± SEM) for three independent experiments is shown. Significance was determined by two-tailed unpaired t test and represented as *, P ≤ 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.001. HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; RelA, RelA proto-oncogene, NF-KB subunit; siCtrl, control siRNA; sip65, p65-targeting siRNA; Nuc, nucleus; Cyt, cytoplasm.