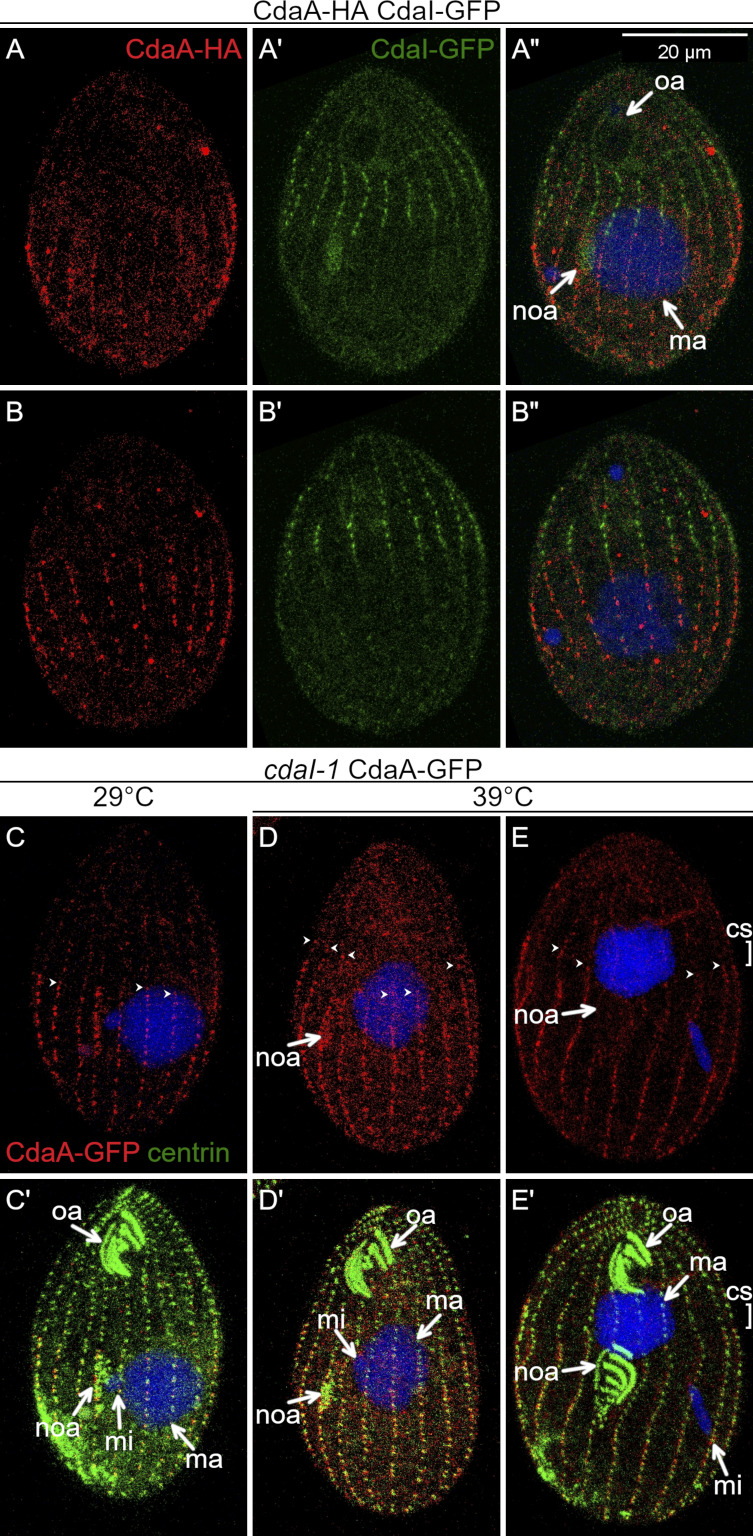
Figure 6.
CdaI excludes CdaA-GFP from the anterior cortical domain. (A–B″) Prior to the cortical subdivision, CdaI and CdaA occupy complementary cortical domains. Two sides of the same cell coexpressing CdaI-GFP (green) and CdaA-HA (red); the fusion proteins are detected by immunofluorescence with anti-tag antibodies, and DNA is stained with DAPI (blue). (C–E′) CdaI excludes CdaA from the anterior cell half. The cells shown are cdaI-1 and express CdaA-GFP (detected with anti-GFP antibodies, red) and are stained with the anti-centrin (green) and DAPI (blue) after growth at either 29°C (C and C′) or 39°C (D–E′). (C and C′) An early divider (before the cortical subdivision) at 29°C. (D and D′) A cdaI-1 cell at the early stage of the oral primordium development, before its migration in the anterior direction. Note that the anterior ends of some of the CdaA-GFP streaks (arrowheads) are abnormally extended into the anterior cell half (compare with Fig. 3, B–C′). (E and E′) A cdaI-1 cell in which the oral primordium has already shifted in the anterior direction and the cortical subdivision has started to develop at that shifted position. The anterior ends of the CdaA-GFP streaks are immediately posterior to the shifted cortical subdivision. cs, cortical subdivision; ma, macronucleus; mi, micronucleus; noa, new oral apparatus (oral primordium); oa, oral apparatus. In C–E, the arrowheads show the anterior ends of some of the CdaA-GFP streaks.