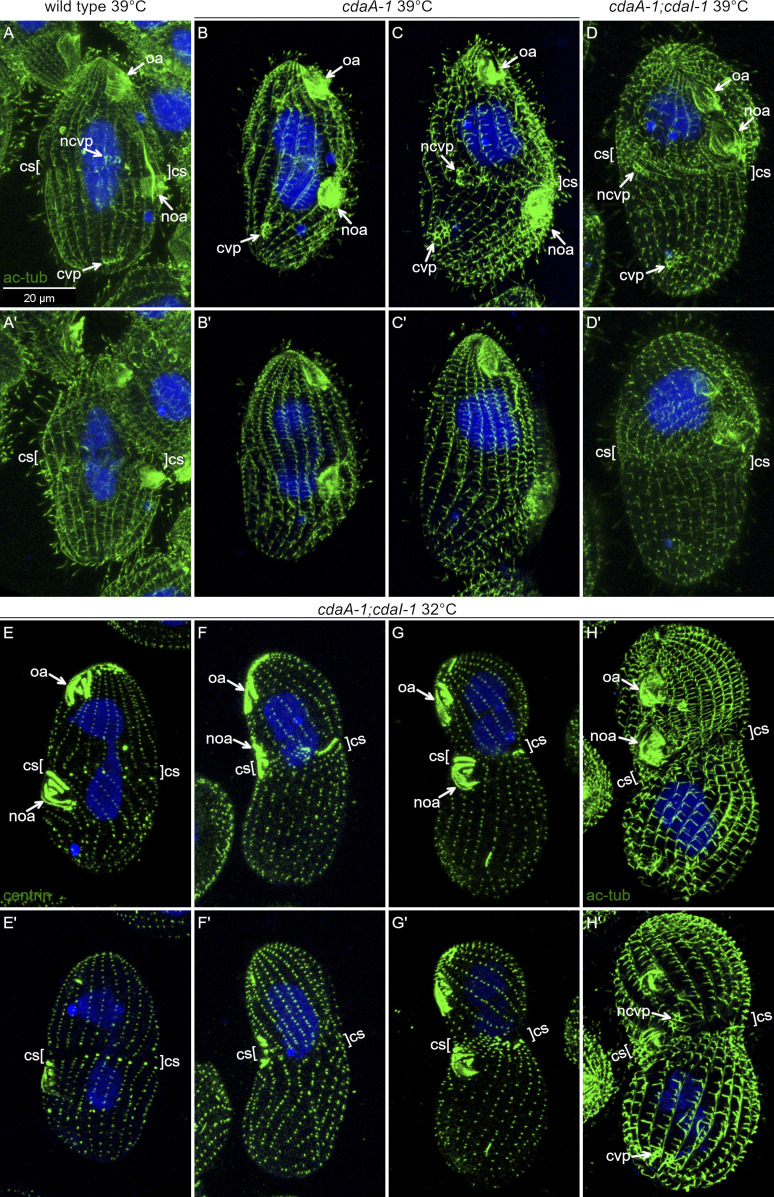
Figure S5.
CdaI and CdaA interact to position new structures. (A–D′) Effects of cdaA-1 and cdaI-1 mutations on positions of new CVPs. Cells were incubated at 39°C for 3 h and labeled with the monoclonal antibody 6–11 B-1 directed against acetyl-K40 α-tubulin (green) that labels ciliary and cortical microtubules, including those forming the CVPs. The nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (A and A′) A dividing wild-type cell. The new CVPs appear anteriorly to the cortical subdivision. (B and B′) A dividing cdaA-1 cell that failed to develop a cortical subdivision. The old CVPs are present but the new CVPs failed to form. (C and C′) A rare dividing cdaA-1 cell that has developed a partial cortical subdivision. The new CVPs are anterior and at the level of cortical subdivision. (D and D′) A double-mutant cdaA-1;cdaI-1 cell. The new CVPs are located at the level of or immediately posteriorly to the cortical subdivision. (E–H′) Double-mutant cdaA-1;cdaI-1 cells after 28-h incubation at 32°C labeled with either the anti-centrin (E–G′) or 6–11 B-1 anti-acetyl-K40 α-tubulin antibody (H and H′) and DAPI. (E and E′) A morphologically normal dividing cdaA-1;cdaI-1 cell. (F–H′). Examples of dividing cdaA-1;cdaI-1 cells with an anterior shift of the division plane. (F and F′) The fission furrow appears to cut through the oral primordium. (H and H′) A dividing cdaA-1;cdaI-1 cell with an anterior shift of the division plane. The CVPs form correctly in relation to the cortical subdivision (resembling cdaI-1 alone). cs, cortical subdivision; cvp, old CVP; ncvp, new CVP; noa, new oral apparatus (oral primordium); oa, oral apparatus.