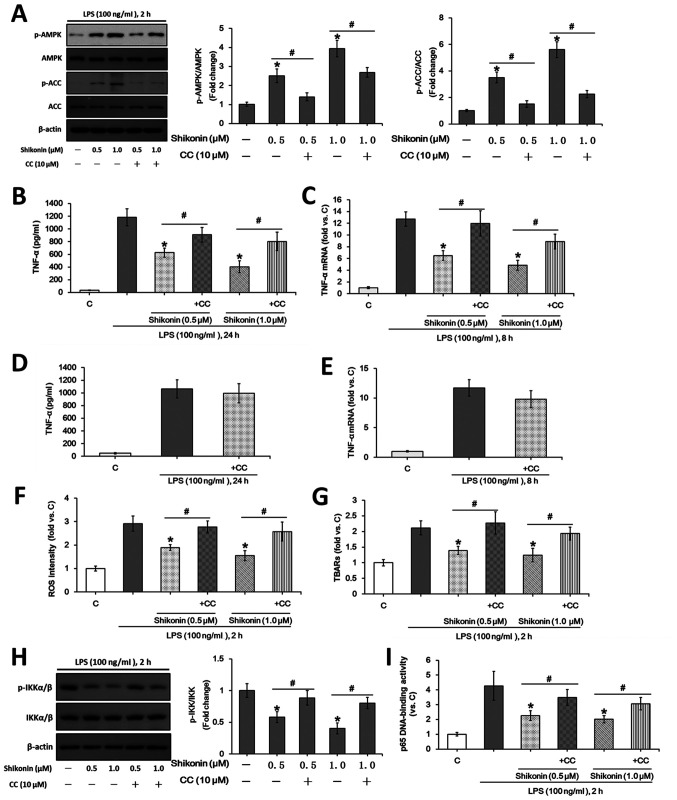
Figure 3.
Non-cytotoxic doses of shikonin suppress LPS-induced TNF-α expression via activating AMPK pathway. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 100 ng/ml of LPS, or in combination with the indicated doses of shikonin with and without 1 h pretreatment of 10 µM compound C. (A) Protein expression levels of ACC, p-ACC, AMPKα and p-AMPKα were determined by western blotting and then semi-quantified by densitometric analysis. (B) Extracellular contents of TNF-α were examined using ELISA assay. (C) Relative mRNA levels of TNF-α were examined using RT-qPCR assay. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 100 ng/ml of LPS with or without 1 h pretreatment of 10 µM compound C for (D) 24 h or (E) 8 h. Extracellular concentration of TNF-α was examined using ELISA assay. Relative mRNA levels of TNF-α were examined using RT-qPCR assay. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 100 ng/ml of LPS for 2 h, or in combination with the indicated doses of shikonin with or without 1 h pretreatment with 10 µM compound C. (F) Relative ROS intensity and (G) TBARs content were detected by flow cytometry and TBARs production assay, respectively. Activation of NF-κB was evaluated by detecting (H) p-IKKα/β and IKKα/β levels, (I) and p65 DNA-binding activity. *P<0.05 vs. LPS alone group. #P<0.05 vs. corresponding shikonin combined with LPS group. C, control; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; p-, phosphorylated; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; IKKα/β, IκB kinase α/β; CC, Compound C; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TBARs, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances.