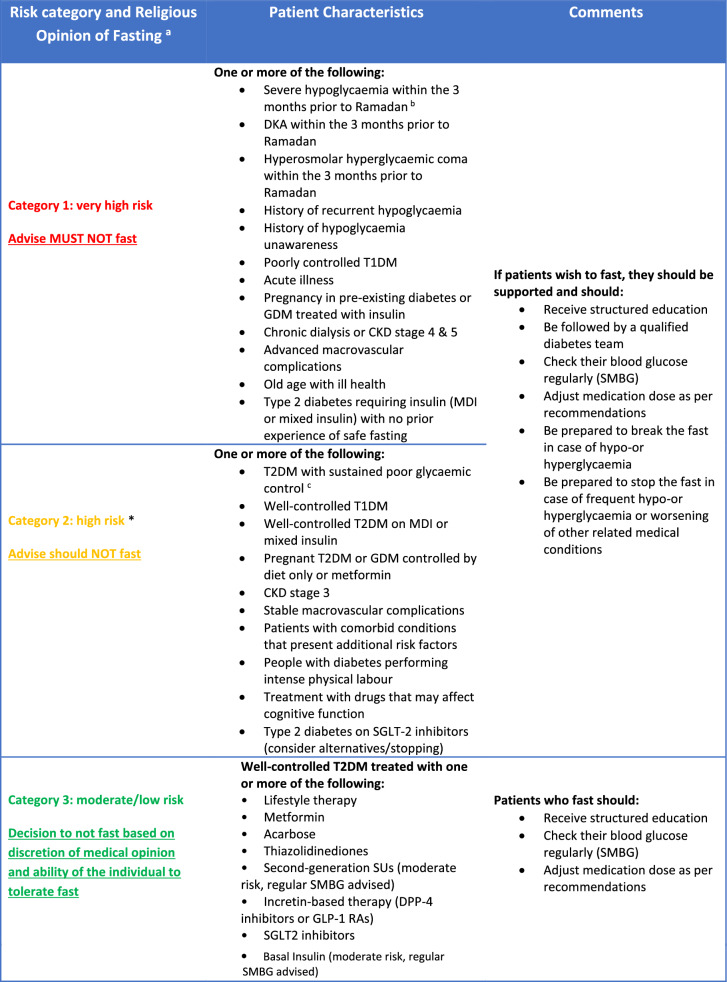
Table 2.
Risk stratification for patients with diabetes
Adapted IDF-DAR risk stratification table, reproduced with permission from the South East London Area Prescribing Committee [97]
CKD Chronic kidney disease, DKA diabetic ketoacidosis, DPP-4 dipeptidyl peptidase-4, GDM gestational diabetes mellitus, GLP-1 RA glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, MDI multiple dose insulin, MTF metformin, SGLT-2 sodium-glucose co-transporter 2, SMBG self-monitoring of blood glucose, SU sulfonylurea, T1DM Type 1 diabetes mellitus, T2DM Type 2 diabetes mellitus
aIn all categories, people with diabetes should be advised to follow medical opinion due to probability of harm. The decision to fast is a personal decision for the person with diabetes, who should be supported by the healthcare professional (HCP) to achieve best possible outcomes
bHypoglycaemia that is not due to accidental error in insulin dose
cThe expected level of glycaemic control is to be agreed upon between HCP and patient according to a multitude of factors. Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) > 75 mmol/mol for >12 months should be used as an indicator of poor control
*Risk upgraded in light of COVID-19 pandemic