Figure 4.
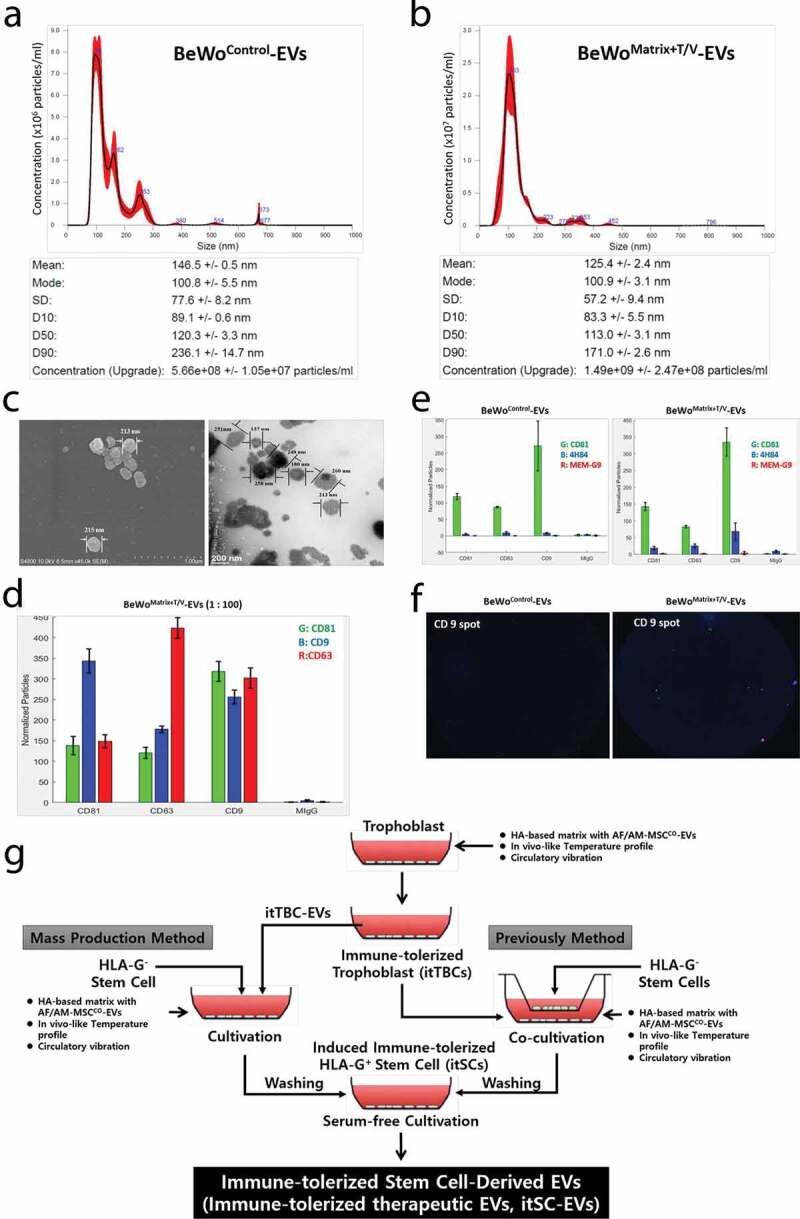
Characterization and Evaluation of itTBC-EVs and a scheme for induction of immune-tolerized stem cells (itSCs) and immune-tolerized EVs (itSC-EVs) through cultivation on HA-MatrixDecidua containing itTBC-EVs with temperature/vibration conditions. (a) NTA analysis of EVs derived from BeWoControl cultured on a general culture plate without temperature/vibration conditions. (b) NTA analysis of EVs derived from BeWoMatrix+T/V cultured on the HA-MatrixDecidua with the in vivo-like temperature change and vibration conditions. BeWoMatrix+T/V-EVs have more EV particles than BeWoControl due to high proliferation rate during invasion to the HA-MatrixDecidua. (c) The images of BeWoMatrix+T/V-EVs using SEM (left) and TEM (right), respectively. (d)The expression of exosomal markers, CD9, CD63, and CD81, on BeWoMatrix+T/V-EVs using ExoView. (e) The expression of HLA-G isoforms in BeWoMatrix+T/V-EVs and BeWoControl-EVs using ExoView. The expressions of 4H84, bound to α1 domain of HLA-G heavy chain (with blue bar), and MEM-G/9, bound to β2 m-associated HLA-G isoforms (with red bar) are much higher in BeWoMatrix+T/V-EVs than BeWoControl-EVs. (F) The images of HLA-G-bound EV spots (blue and red) captured with CD9 antibody using ExoView. (g) A diagram for two methods to induce immune-tolerized stem cells (itSCs) and immune-tolerized EVs (itSC-EVs), by co-cultivation with itTBCs (right) and by using itTBC-EVs (left) under the Ex-vivo culture system established herein.
