Figure 4.
E. coli -induced EV release by moDC.
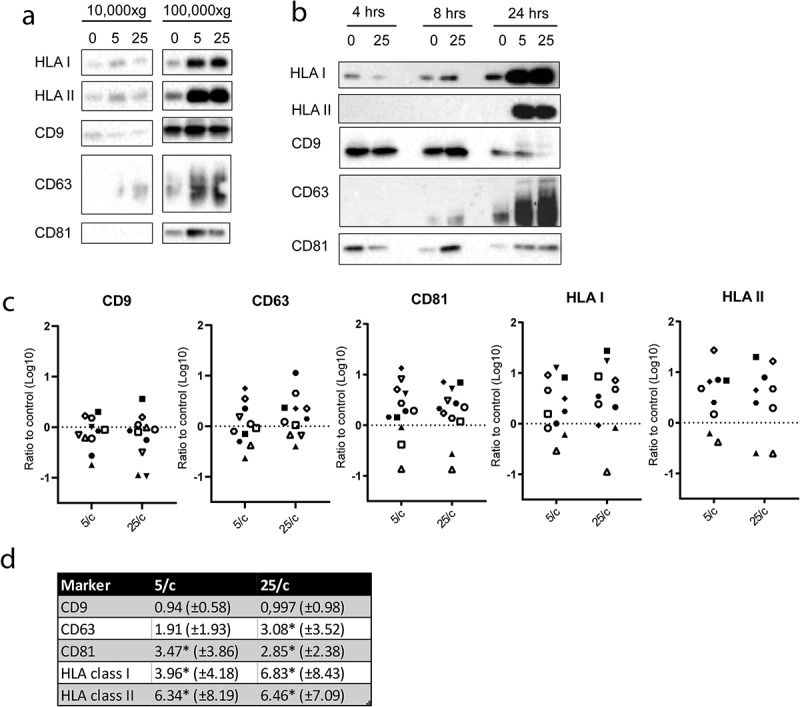
(a) Representative immunoblots from 11 independent experiments detecting HLA-I, HLA-II, CD9, CD63 and CD81 in EV isolated from the culture media from moDC that were incubated for 24hours in the presence of LPS only (0) or presence of both LPS and 5 or 25 E. coli per moDC. Samples of the sequentially harvested 10,000 × g and 100,000 × g pellets were loaded and detected on the same blot (exemplified in supplementary figure 3). (b) Representative immunoblot of EV markers in 100,000 × g pellets from culture media from moDC that were incubated for 4, 8, or 24hours either in the presence of LPS only (0) or in the presence of both LPS and 5 or 25 E. coli per moDC. (c) Quantification of signals as in (b) from 11 independent experiments of appropriately exposed immunoblots of EV pelleted at 100,000 × g from culture media of 24 hour treated moDC. Each symbol corresponds to 1 individual donor. Signal strength induced by 5 or 25 E. coli per moDC is plotted relative to the signal in the absence of E. coli within the same experiment, and fold increase is expressed on a log10 scale. (d) Statistical analysis of fold increase of signals as determined in c (mean ± SD; * indicates significant increase with p≤0.05).
