Figure 5.
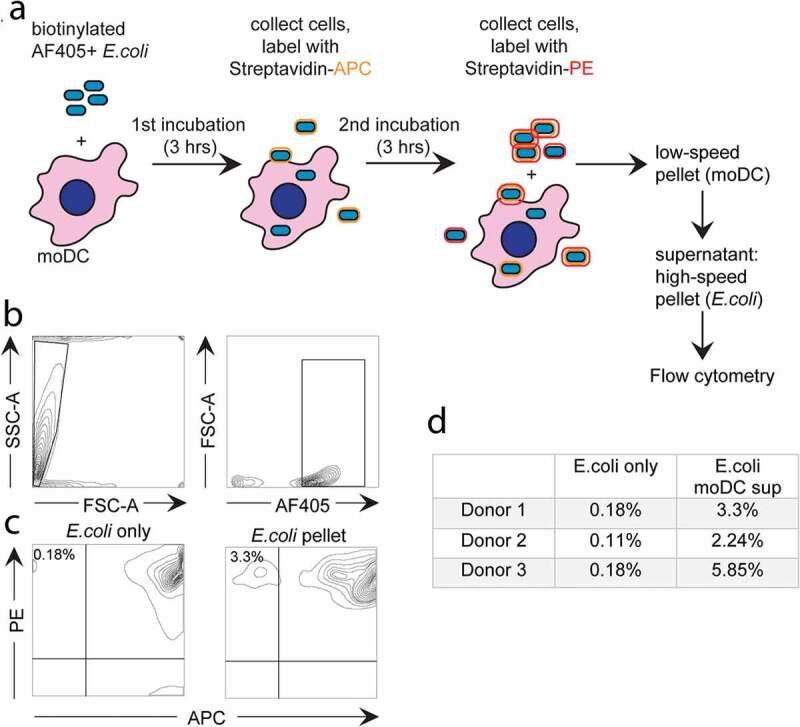
Flow cytometry-based analysis of E. coli expulsion by moDC.
(a) Schematic presentation of the experimental design. MoDC were incubated for 3hours with E. coli that was labelled with both biotin and AF405 (blue). Subsequently, all moDC and some E. coli were collected by centrifugation for 8minutes at 260 × g, leaving the majority of non-phagocytosed E. coli in the supernatant. Pelleted cells were incubated with streptavidin-APC (orange), labelling those biotinylated E. coli that were co-pelleted with the moDC but not phagocytosed. Subsequently, moDC were incubated for another 3hours at 37°C, cooled to 4°C, and stained with streptavidin-PE (red). moDC together with some E. coli were removed by centrifugation at 260 × g, and E. coli remaining in the moDC supernatant were pelleted by a subsequent centrifugation step at 13,300 × g. Expulsed E. coli was identified by flow cytometry as AF405+, APC-, PE+ events. (b) Gating strategy for E. coli: E. coli-sized particles were gated based on scatter and AF405 signal. (c) Flow cytometry plots showing labelling efficiency in a control (“E. coli only”, left panel) and expulsed E. coli (APC-, PE+, “E. coli pellet”, right panel). (d) Amount of expulsed E. coli as percentage of total extracellular E. coli, according to three independent experiments as in c.
