Figure 1.
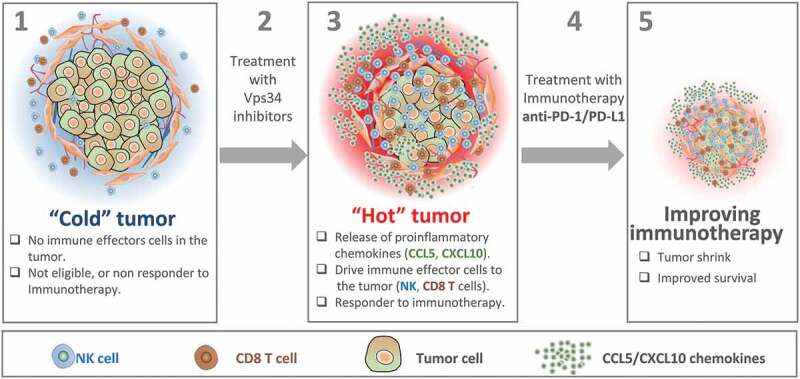
Vps34 inhibition improves anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy by switching cold into hot tumors. Cold tumors are characterized by the absence of immune cells or the limited number of cytotoxic immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Therefore, cold tumors are not eligible or most likely not responding to immunotherapy (1). Treatment of cold tumors with Vps34 inhibitors (2) induces the release by tumor cells of proinflammatory chemokines such as CCL5 and CXCL10. These chemokines drives more NK and CD8 T cells to the tumor microenvironment. Vps34i-treated tumors become hot and therefore eligible to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 based immunotherapy (3). Combined Vps34i with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 (4) improves the therapeutic benefit of immunotherapy and significantly decreases the tumor growth.5
