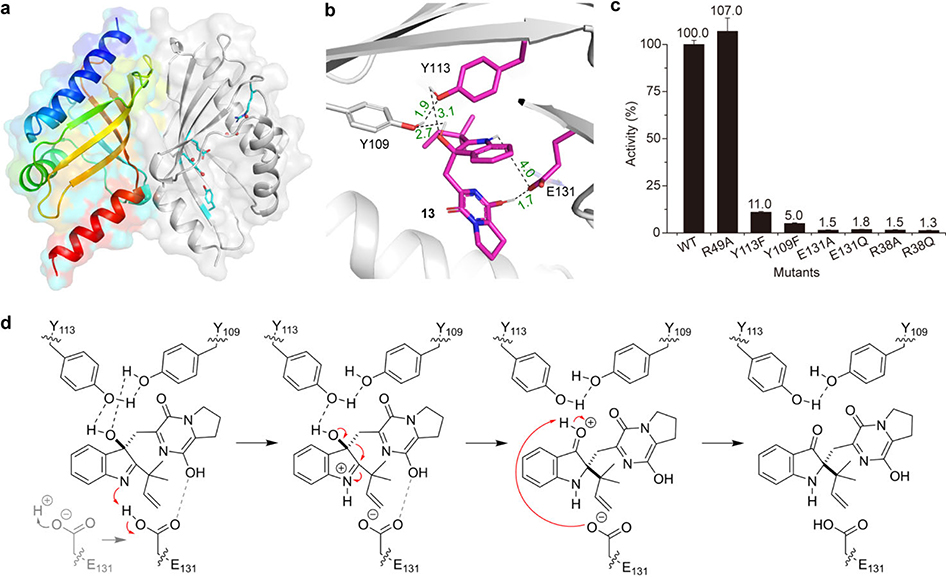
Fig. 5. BvnE crystal structure, docking and the proposed catalytic mechanism.
a, Structure overview of BvnE: left chain shown in rainbow spectrum from N-terminus (blue) to C-terminus (red); the right chain in grey cartoon with putative catalytic acid-basic residues (cyan) and water molecules in the active site (red spheres). b, BvnE-13 complex with key residues and hydrogen bonding shown. c, Site-directed mutagenesis results; Data represent the average of triplicated independent experiments (centre values, means; error bars, standard deviations; n = 3). d, The proposed BvnE reaction mechanism for isomerization of 13. Glu131-mediated proton transfer could be assisted by 540 Arg38, which interacts with Glu131 via an ordered water network (Supplementary Fig. 62c). Indirect deprotonation of the oxonium intermediate via bound solvent molecules rather than a direct interaction with Glu131 cannot be excluded.