Figure 2.
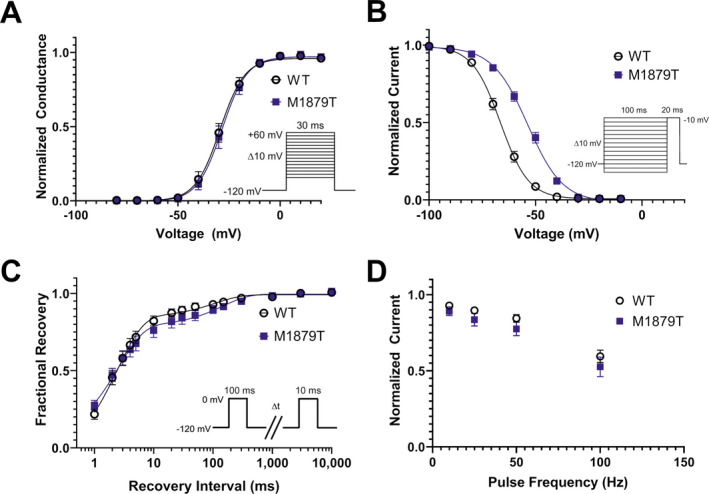
M1879T affects voltage dependence of inactivation. (A) Voltage dependence of activation of WT (n = 14) and M1879T (n = 14) channels determined using the voltage protocol shown as an inset. There was no difference in activation V 1/2 between WT and M1879T (P = 0.51 by Mann–Whitney U test). (B) Voltage dependence of inactivation of WT (n = 18) and M1879T (n = 25) channels (voltage protocol shown as an inset). There was a significant depolarizing shift in inactivation V 1/2 (P < 0.0001 by Mann–Whitney U test). (C) Time course of recovery from inactivation after 100 msec depolarization (protocol shown as inset) comparing WT (n = 10) and M1879T (n = 10). There were no significant differences in time constants for recovery from inactivation between WT and M1879T (P > 0.05 by Mann–Whitney U test; Table 1). (D) Plot of residual current (comparing 300th pulse to 1st pulse) after repetitive pulsing to 0 mV at the indicated frequency (n = 7 for WT and n = 7 for M1879T). There were no significant differences between WT and M1879T at any frequency (P > 0.05 by Mann–Whitney U test).
