Figure 1. The mechanism for antifibrotic actions of nintedanib.
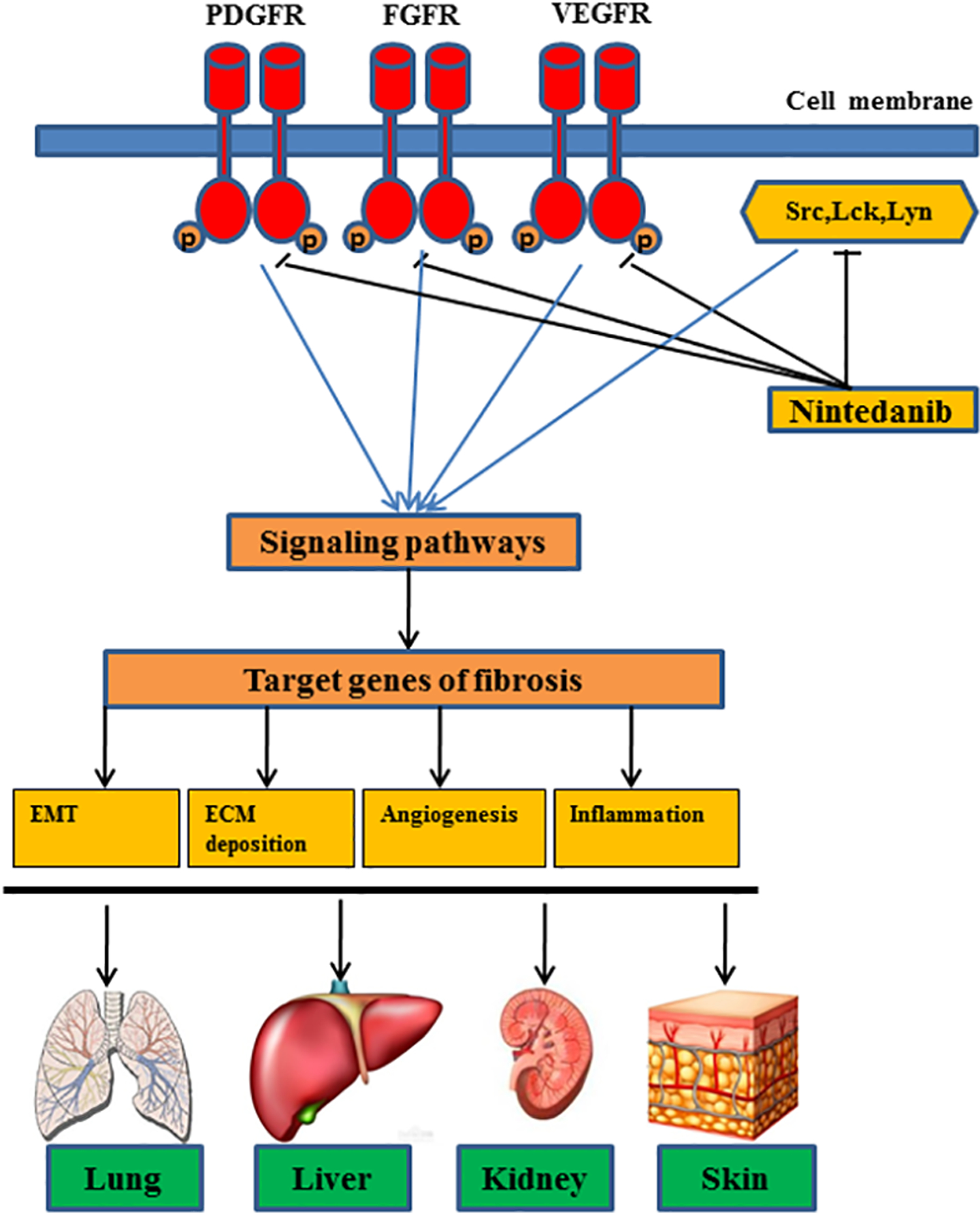
Nintedanib inhibits both tyrosine kinase receptors, including platelet-derived growth factor receptors, fibroblast growth factor receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and non-receptor kinases, such as Src, c-Abl, c-kit, leading to inactivation of their downstream stream signaling pathways and targeted profibrotic genes responsible for the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, angiogenesis and inflammation responses in multiple organs (i.e. lung, liver, kidney and skin).
