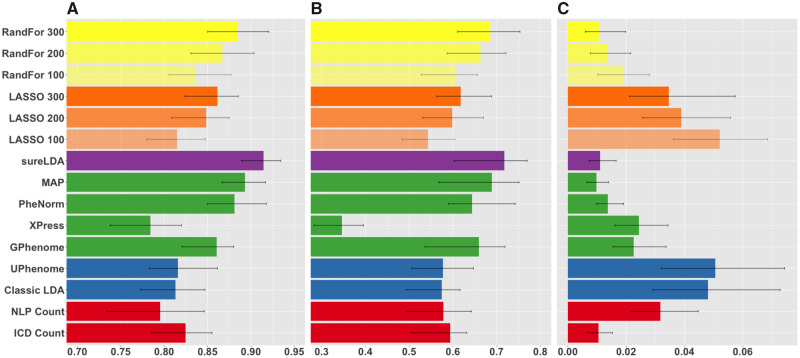
Figure 4.
Mean (A) areas under the receiver-operating characteristic curves, (B) F-scores, and (C) label rank losses of phenotype predictions on real diseases from the Partners HealthCare Biobank comparing raw International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and natural language processing (NLP) surrogates (red), fully unsupervised phenotyping methods (blue), alternative weakly supervised methods (green), surrogate-guided ensemble latent Dirichlet allocation (sureLDA) (purple), supervised phenotyping using LASSO regularized logistic regression (orange), and random forest (RandFor) (yellow) with 100-300 true labels. Error bars reflect empiric bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals. GPhenome: grounded phenome; MAP: multimodal automated phenotyping.