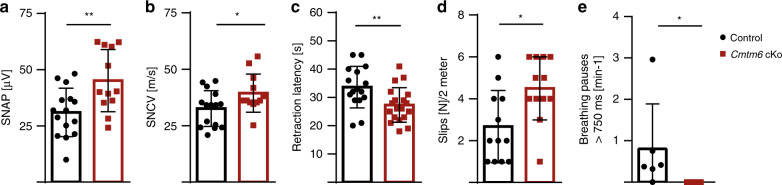
Fig. 3. Electrophysiological properties and behavioral performance of mice lacking CMTM6 from Schwann cells.
a, b Electrophysiological measurement reveals a larger sensory nerve action potential (SNAP) and accelerated sensory nerve conduction velocity (SNCV) in the tails of Cmtm6-cKo compared to control mice at P75. n = 15 control and n = 12 Cmtm6-cKo mice; a P = 0.0061 and b P = 0.0386 by two-tailed Student’s t-test. c The latency of retracting a hindlimb upon a heat stimulus was reduced in Cmtm6-cKo compared to control mice. n = 16 control and n = 19 Cmtm6-cKo mice; P = 0.0089 by two-tailed Student’s t-test. d Compared to control mice, Cmtm6-cKo-mice showed an increased number of fore- and hindlimb slips while traveling a distance of 2 m on a regular grid. n = 12 mice per genotype; P = 0.0111 by two-tailed Student’s t-test. e Cmtm6-cKo-mice did not show breathing pauses longer than 750 ms. n = 6 mice per genotype; P = 0.0152 by two-sided Mann–Whitney rank-sum test. Data presented as mean ± SD; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Source data see Source Data file.