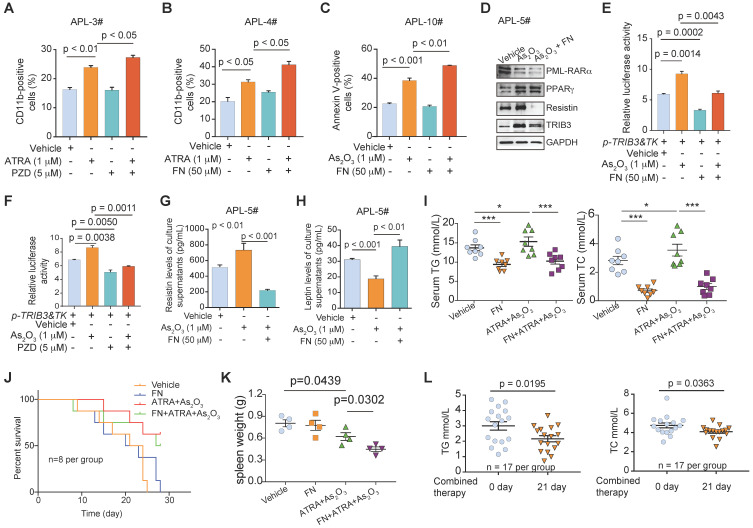
Figure 8.
PPAR agonists induce the synergism of anti-APL with ATRA/As2O3 by improving dyslipidemia. (A) CD11b expression was evaluated by flow cytometry in primary APL cells that were subjected to the indicated treatment. The percentage of CD11b-positive cells was calculated with FCS Express software. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM of 3 assays. (B and C) The PPARα agonist (fenofibrate, FN) increased the percentage of differentiated and apoptotic APL cells induced by ATRA or As2O3 treatment. Primary APL cells were treated with the indicated treatment for 24 h and then stained with a CD11b antibody or Annexin-V‑PI and evaluated by flow cytometry. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM of 3 assays. (D) The expression of PML-RARα, PPARγ, TRIB3, and resistin in primary APL cells treated as indicated was detected by Western blotting. (E and F) PPAR agonists suppressed the elevated TRIB3 transcription induced by As2O3. HEK 293T cells were transiently transfected with the TRIB3 reporter plasmids (p-TRIB3&TK). After 24 h of transfection, the cells were treated with the indicated treatment for 24 h, and luciferase activities were then measured. (G and H) The PPARα agonist (FN) enhanced the secreted leptin level and reduced the resistin level in primary APL cells that were subjected to As2O3 treatment. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM of 3 assays. (I) Serum TG and TC levels in Pml-Rarα recipient FVB mice treated as indicated. (J) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the Pml-Rarα recipient FVB mice treated as indicated (n = 8). (K) The data indicate the spleen weights of the Pml-Rarα recipient FVB mice treated as indicated. (L) Serum TG and TC levels in APL patients (n = 17) were evaluated after combined treatment with ATRA/arsenic plus FN.