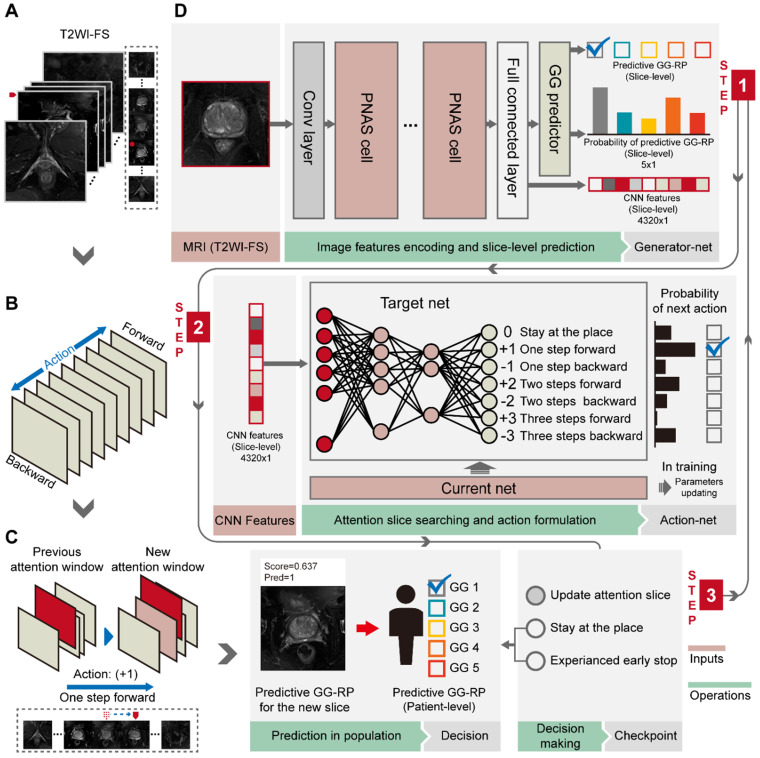
Figure 3.
Workflow of PCa-GGNet. (A) The input of PCa-GGNet, for which only one slice was input per operation. The initial input was the median slice of the whole T2WI-FS sequence. (B) Action rules for attentional slice searching, which included direction and step length of actions. (C) The illustration of attentional slice searching and updating. (D) The workflow and architecture of PCa-GGNet. PNAS refers to a progressive neural architecture search. In the first step, we selected the median slice of T2WI-FS as input for the convolutional neural network (CNN)-based model to predict GG-RP on each slice. For the second step, we used features from the first step of the DRL-based model to generate an action for updating input. For the third step, a checkpoint was used to determine whether the results of the current input could be used as patient-level predictions. If so, the input was a decision slice. If not, our attention was changed through actions to find a new slice as an input. The framework was a sequential method to predict patient-level GG-RP. The gray arrow shows a forecasting process. See Methods for complete details.