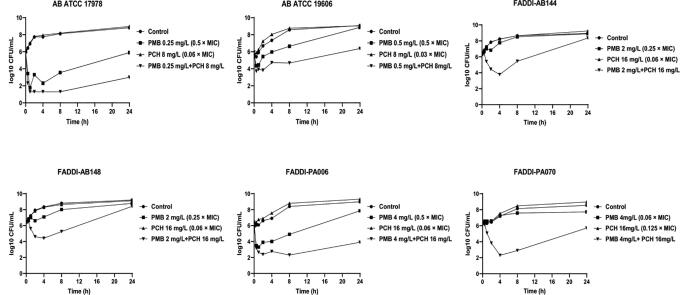
Fig. 2.
Time kill curves for polymyxin B and prochlorperazine monotherapies and in combinations against polymyxin-resistant P. aeruginosa strains, FADDI-PA070 (polymyxin B MIC = 64 mg/L, prochlorperazine MIC = 128 mg/L) and FADDI-PA006 (polymyxin B MIC = 8 mg/L, prochlorperazine MIC > 128 mg/L); against polymyxin B-susceptible A. baumannii strains, ATCC 19606 (polymyxin B MIC = 1 mg/L, prochlorperazine MIC > 128 mg/L) and ATCC 17978 (polymyxin B MIC = 0.5 mg/L, prochlorperazine MIC = 128 mg/L); and against polymyxin B-resistant A. baumannii strains FADDI-AB148 and FADDI-AB144 (polymyxin B MIC = 8 mg/L, prochlorperazine MIC > 128 mg/L for both strains).