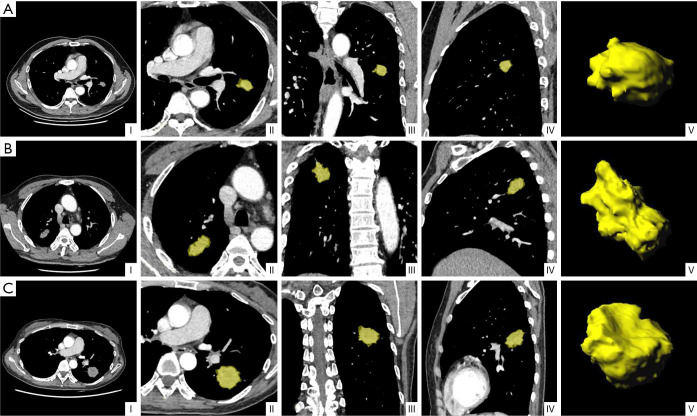
Figure 4.
Representative CT images with tumor segmentation by the radiomics analysis platform. (I) Axial views show a lobulated lung tumor for image segmentation. (II) Axial view, (III) coronal view, and (IV) sagittal view showed segmented lung tumors indicated by a yellow overlay. (V) Three-dimensional views of the segmented tumors. (A) (I-V) A 61-year-old male non-smoker, with EGFR wild-type lung adenocarcinoma. CT mediastinal window showed a solid mass in the upper lobe of the left lung with lobulation sign and a maximum diameter of about 20 mm. (B) (I-V) A 58-year-old male smoker, with lung adenocarcinoma of EGFR exon-19 deletion. CT mediastinal window showed a solid mass in the upper lobe of the right lung with a maximum diameter of about 35 mm, rough margin, and lobulated sign. (C) (I-V) A 48-year-old female non-smoker, with lung adenocarcinoma of EGFR exon-21 L858R mutation. CT mediastinal window showed a solid mass in the lower lobe of the left lung with a maximum diameter of about 36 mm, burrs, and lobulation. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor.