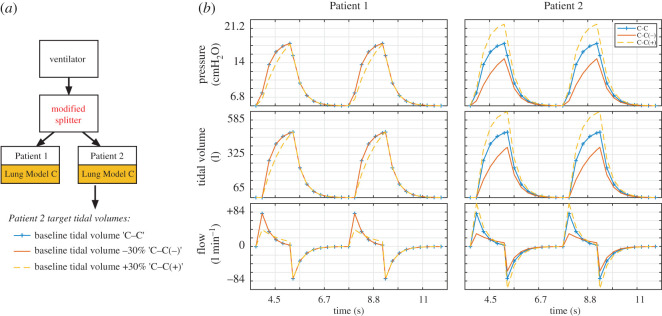
Figure 6.
Using the modified splitter to adjust tidal volume in Patient 2 independent of tidal volume in Patient 1. (a) In this experiment, two patients with identical respiratory compliance (Lung Model C) are connected via the modified splitter to the ventilator. Target tidal volumes were either baseline (blue), −30% (red, C–C(–) model) or +30% (dotted yellow, C–C(+) model). (b) Pressure–time, tidal volume–time and flow–time graphs. Ventilation was performed in pressure control mode with PIP 17 cmH2O, PEEP 5cmH2O, RR 15 breaths/min, I : E ratio 1 : 2. Using these settings, a tidal volume of 493 ml was achieved for both Patient 1 and Patient 2 (blue lines). The variable resistance in the inspiratory limb supplying Patient 2 was then increased, reducing Patient 2 tidal volume while Patient 1 tidal volume remained unchanged (red lines, C–C(–) model). To increase Patient 2 tidal volume from baseline, PIP was increased to 20.67 cmH2O but the variable resistance in the inspiratory limb supplying Patient 1 was also increased to return Patient 1 tidal volume to baseline (dotted yellow lines).