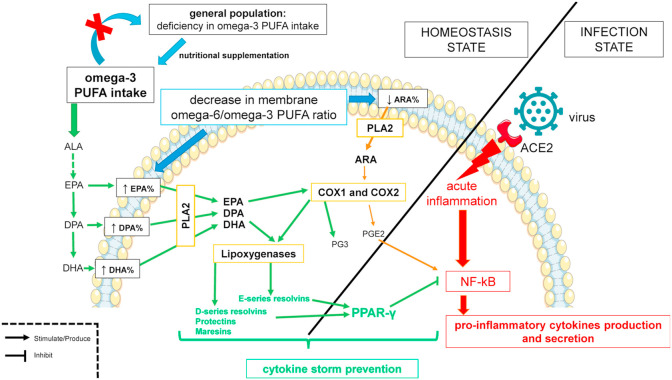
Fig. 1.
– Expected mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effect of omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega-3 LC-PUFAs) and cytokine storm prevention during the Coronavirus disease-2019. General population has deficiency in Omega-3 LC-PUFAs that increases proportion of arachidonic acid (ARA) from Omega-6 PUFA family in phospholipid membranes of the cells. ARA is liberated from its sn-2 position by the phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and become a substrate for cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX1 and COX2). Prostaglandins E2 (PGE2) is synthesized from ARA and is pro-inflammatory by activating NF-κB and lead to systemic chronic low-grade inflammation and a higher response to severe acute inflammation. A nutritional supplementation in omega-3 fatty acids may decrease or even remove the deficiency in population. This supplementation will increase eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), omega-3 DPA and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) proportion in phospholipid membranes of the cells. EPA, DPA and DHA are, like ARA, liberated by PLA2. It is a limiting step for the synthesis of lipid mediators from PUFAs. EPA is a substrate for COX enzymes and also lipoxygenases (LOX). PGE3 and E-series resolvins are produced from EPA and have anti-inflammatory properties. DHA is a substrate for LOX and produces D-series resolvins, protectins and maresins that have anti-inflammatory properties. These specialized pro-resolving mediators from EPA and DHA, in a case of acute inflammation by activation of NF-κB, will activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ. PPAR-γ inhibits NF-κB. Consequently, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines is reduced and may prevent cytokine storm.