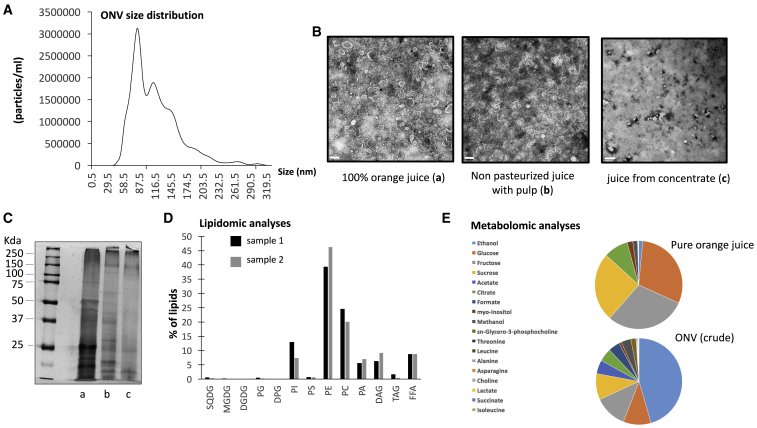
Figure 1.
Characterization of ONVs
(A) ONV pellet size distribution isolated from pure orange juice, by nanoparticle tracking analyses. (B) TEM of ONV pellets extracted from different preparations of orange juices (scale bars, 200 nm for a and b, or 500 nm for c). (C) Polyacrylamide gel of ONV proteins detected with silver staining (a, pure juice; b, unpasteurized juice; c, reconstituted from concentrated juice). (D) Lipids identified in 1 mg of ONV pellet expressed as percentage of total lipids. The two colors represent two lipidomic analyses from two ONV preparations. SQDG, sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol; MGDG, monogalactosyldiacylglycerol, DGDG, digalactosyldiacylglycerol, PG, phosphatidylglycerol; DPG, diphosphatidylglycerol (or cardiolipin); PI, phosphatidylinositol; PS, phosphatidylserine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PA, phosphatidic acid; DAG, diacylglycerol; TAG, triacylglycerol; FFA, free fatty acids. Full lipid composition is indicated in Figure S2. (E) Metabolites found in orange juice or ONVs identified by proton nuclear magnetic resonance. Data are expressed as % of total for each condition. The full metabolomic data are provided in Table S1. Only metabolites from crude ONVs are shown because they were prepared using the same conditions as for pure orange juice.