Figure 4.
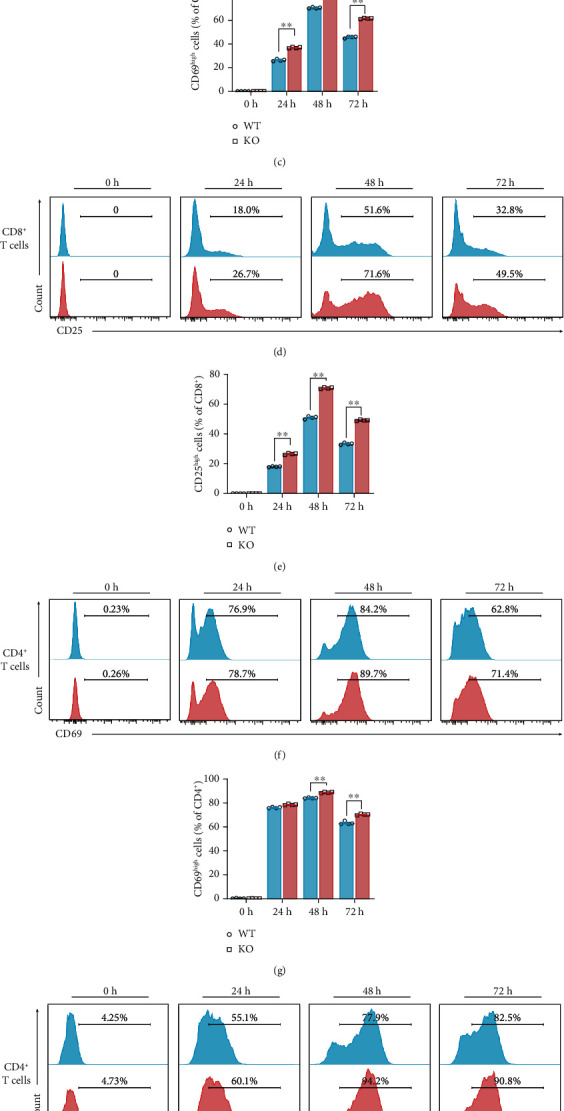
Sirt5 KO naïve T cell activation is promoted in vitro. (a) Scheme of experimental design. Mouse naïve T cells were purified from spleens of WT/KO mice and activated by anti-CD3/CD28. After culturing for 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h, cells were collected and analyzed by flow cytometry. (b) Representative histograms of CD69 of naïve CD8+ T (0 h) and CD8+ T cells activated for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h using flow cytometry. (c) Frequency of cells highly expressing CD69 among CD8+ T cells cultured for 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. (d) Representative histograms of CD25 of naïve CD8+ T (0 h) and CD8+ T cells activated for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h using flow cytometry. (e) Frequency of cells highly expressing CD25 among CD8+ T cells cultured for 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. (f) Representative histograms of CD69 of naïve CD4+ T (0 h) and CD4+ T cells activated for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h using flow cytometry. (g) Frequency of cells highly expressing CD69 among CD4+ T cells cultured for 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. (h) Representative histograms of CD25 of naïve CD4+ T (0 h) and CD4+ T cells activated for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h using flow cytometry. (i) Frequency of cells highly expressing CD25 among CD4+ T cells cultured for 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; two-tailed unpaired t-test.
