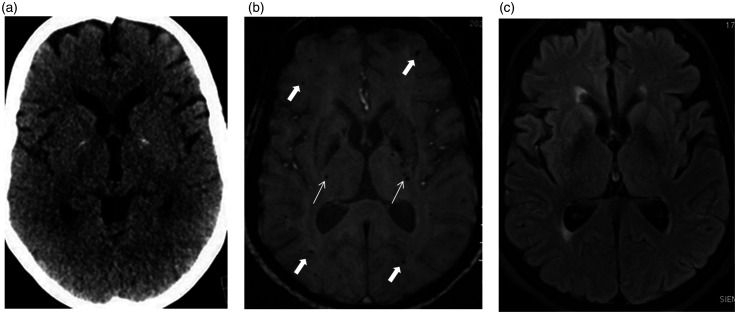
Figure 2.
Axial unenhanced computed tomography (CT) scan (a) at the level of the basal ganglia and thalami appear unremarkable, except for physiological-basal ganglia calcifications. Axial susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (b) shows widespread blooming hypointense foci consistent with microbleeds predominantly involving the juxtacortical white matter (thick arrows), sparing the deep periventricular white matter, basal ganglia and thalami. Basal ganglia calcifications are hypointense on SWI. Note bilateral tiny microbleeds in the internal capsules (thin arrows). Axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image (c) at this level appears unremarkable.