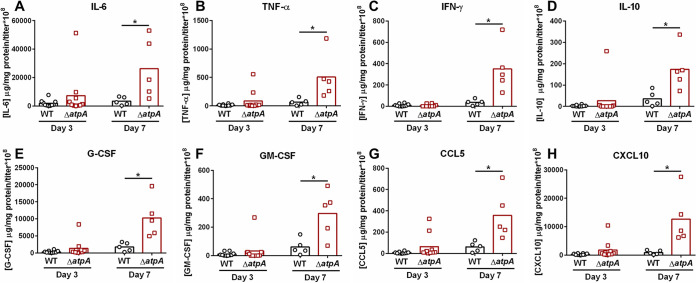
FIG 6.
S. aureus AtpA attenuates inflammatory mediator production during prosthetic joint infection (PJI). C57BL/6NCrl mice were infected with 103 CFU of S. aureus WT or ΔatpA using a model of PJI. Implant-associated tissue was collected at days 3 or 7 postinfection, and inflammatory mediators quantified using a multianalyte bead array. IL-6 (A), TNF-α (B), IFN-ɣ (interferon-gamma) (C), IL-10 (D), G-CSF (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor) (E), GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor) (F), CCL5 (regulated upon activation T cell expressed and secreted; RANTES) (G), and CXCL10 (interferon-inducible protein 10 kDa) (H) concentrations were normalized to the protein concentration per sample and bacterial titer of each mouse to correct for differences in infectious burden between WT and ΔatpA. Results from day 3 represent the mean combined from 2 independent experiments (n = 10 mice/group) and day 7 from one experiment (n = 5 mice/group). Significant differences are denoted by asterisks (*, P < 0.05; Student's t test with Holm-Sidak correction).