Figure 6. Proposed model by which IRR dynamically regulates CPK28 immunomodulatory buffering of PEPR-mediated immunity.
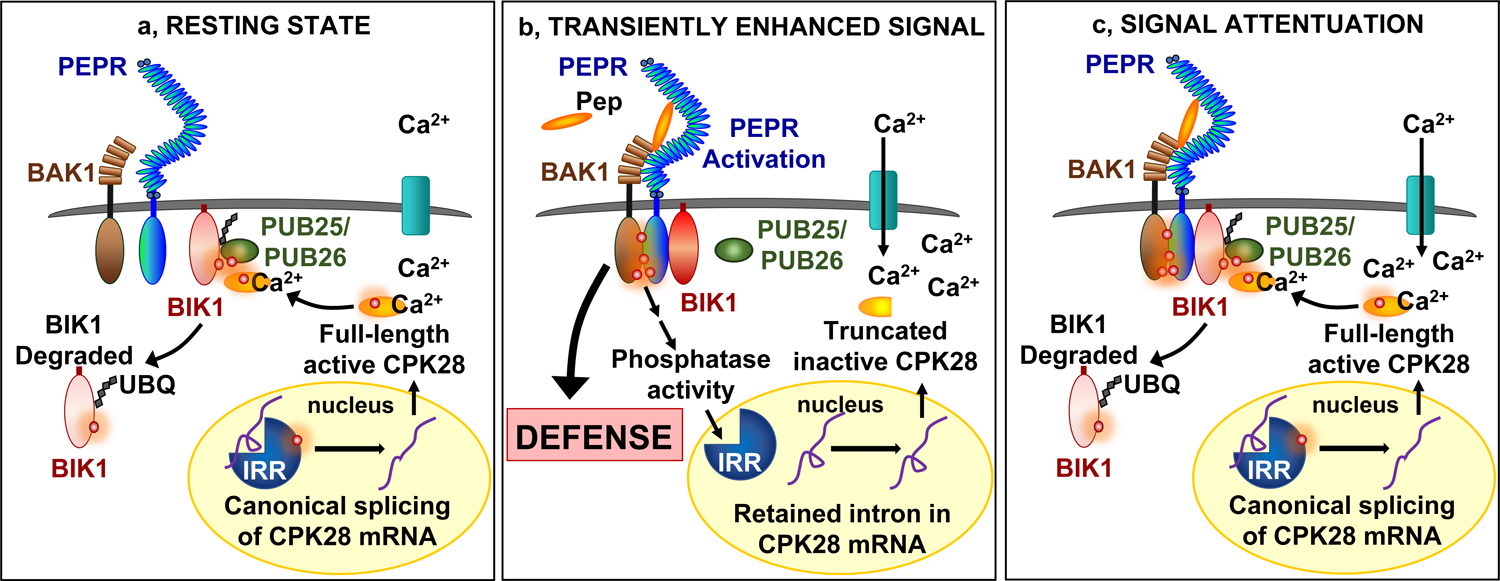
a, Resting state: phosphorylated IRR associates with transcripts encoding CPK28, facilitating canonical splicing into mRNA that produce a full-length protein which functions as a negative regulator of immune receptor complex signaling by phosphorylating PUB25/26 ubiquitin ligases to promote ubiquitylation and subsequent degradation of BIK1. b, Transiently enhanced signal: AtPep1 activates PEPR receptor complexes, leading to transient dephosphorylation of IRR and dissociation from CPK28 transcripts, resulting in temporary accumulation of a retained intron variant encoding a premature stop codon that yields a truncated and inactive CPK28 protein variant, reducing CPK28 buffering of the receptor complex and resulting in amplified PEPR-mediated immune signaling and defense output. c, Signal attenuation: recovery of IRR phosphorylation reestablishes association with CPK28 transcript to promote canonical splicing and resumed translation of a full-length protein to reinstitute negative regulation of PEPR signaling and immunity
