Fig. 5.
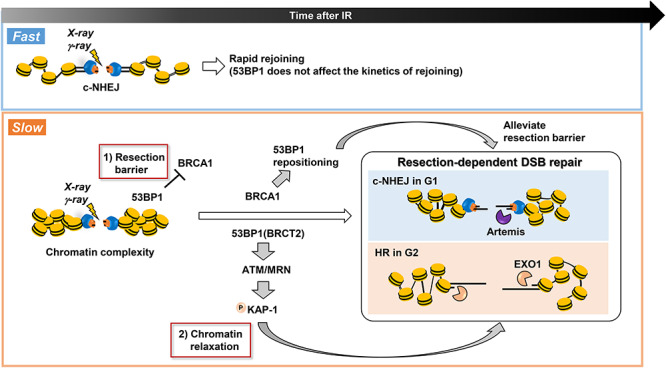
53BP1 has two roles in IR-induced DSB repair: it functions as a resection barrier and is essential for HC-DSB repair. As stated above, most DSBs are repaired with fast kinetics by c-NHEJ in G1 and G2 phase. In G1 phase, 20% of DSBs are repaired by resection-dependent c-NHEJ and a similar subset of DSBs are repaired by HR in G2 phase (note: HR also repairs TA-DSBs in G2 phase). Both HR and resection-dependent c-NHEJ involve some level of resection (greater for HR compared to resection-dependent c-NHEJ) and 53BP1 poses a barrier to both processes, which is relieved by BRCA1 (item 1 and the upper arrow of the figure). Additionally, these DSBs appear to be located in regions of high chromatin complexity (heterochromatin regions) and necessitate chromatin relaxation prior to rejoining. 53BP1 is essential for this process, which involves the tethering of MRN, ATM recruitment and focused phosphorylation of KAP1 (item 2 and the lower arrow of the figure). These two distinct roles of 53BP1 are required for both resection-dependent c-NHEJ in G1 and HR repair of these specific DSBs in G2.
