Figure 1.
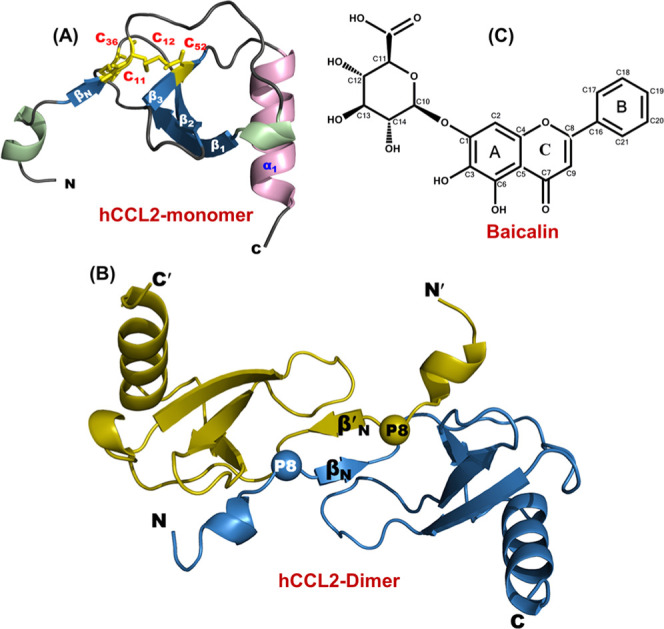
Structural characteristics of CCL2 protein and baicalin (BA): (A) Three-dimensional structure of human CCL2 protein’s monomeric subunit depicting all of the structural elements (PDB ID: 1dok). The structure comprises a long N-terminal, three antiparallel β-strands, and a C-terminal α-helix. The disulfide bonds are highlighted in yellow (stick representation). (B) Three-dimensional structure of the human CCL2 dimer (PDB ID: 1dok). The proline residues involved in the arm-exchange process are represented by spheres. (C) Chemical structure of flavonoid baicalin (BA).
