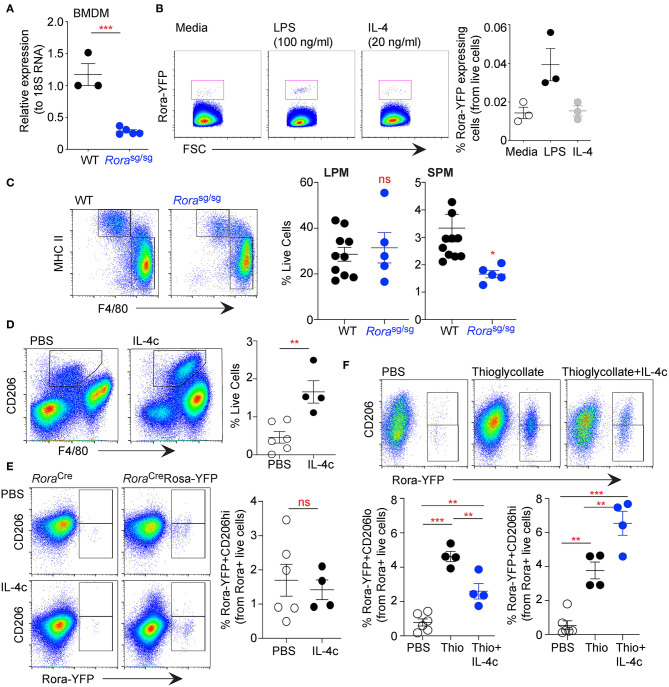
Figure 5.
RORα acts specifically on myeloid-derived macrophages, with limited effect on tissue resident cells. Bone-marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were isolated from age-matched WT and Rorasg/sg mice and expression of Rora determined by qRT-PCR relative to 18S (A, n = 3 WT, n = 5 Rorasg/sg). BMDM isolated from RoraCreRosa-YFP mice were stimulated with media-alone, LPS (100 ng/ml) or IL-4 (20 ng/ml) for 48 h and YFP+ve cells determined by flow cytometry (B, n = 3). Peritoneal exudate cells were collected from age-matched WT and Rorasg/sg mice by peritoneal lavage and stained for flow cytometry as small peritoneal macrophages (SPM; Live/dead−CD45+CD11b+SiglecF−F4/80+MHC class IIhi) or large peritoneal macrophages (LPM; Live/dead−CD45+CD11b+SiglecF−F4/80hiMHC class IIlo) (C; n = 10 WT; n = 5 Rorasg/sg). RoraCreRosa-YFP mice were injected i.p. with PBS (n = 6) or IL-4c (n = 4) on days 0 and 2 (D,E), or thioglycollate (day 0; n = 4) with or without IL-4c (days 0 and 2; n = 4) (F). Increase in CD206+ macrophages in the peritoneal cavity of mice following IL-4c treatment (D, gated as Live/dead−CD45+CD11b+SiglecF−F4/80+CD206+). Flow cytometry was performed on LPM (gating as above; E) or SPM (gating as above; F) assessing Rora-YFP expression on CD206hi and CD206lo cells. Data is representative of mean ± SEM. Student's t-test or ANOVA (E) was used for statistical analysis: ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.