Figure 6.
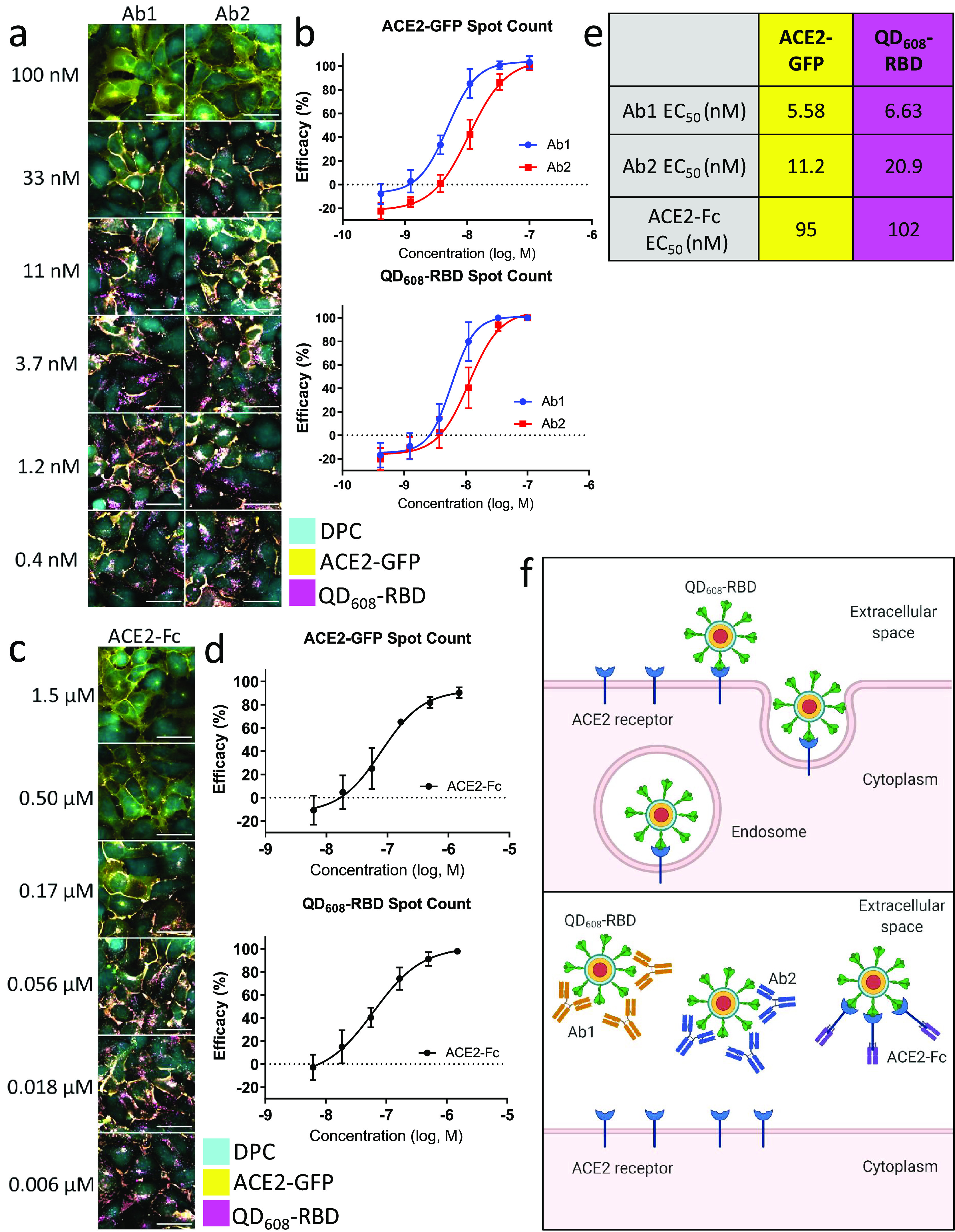
Neutralizing antibodies and ACE2-Fc block QD608-RBD-induced endocytosis. (a) Representative image montage of ACE2-GFP (yellow) HEK293T clone 2 treated with 10 nM QD608-RBD (magenta). Digital phase contrast (cyan) was used during live-cell imaging to identify cell bodies. Cells were treated with neutralizing antibodies Ab1 and Ab2 starting at 100 nM. (b) High-content analysis averages for ACE2-GFP and QD608-RBD spot count treated with neutralizing antibodies. (c) Representative image montage of ACE2-GFP (yellow) HEK293T clone 2 treated with 10 nM QD608-RBD (magenta). Digital phase contrast (cyan) was used during live-cell imaging to identify cell bodies. Cells were treated with ACE2-Fc starting at 1.5 μM. (d) High-content analysis averages for ACE2-GFP and QD608-RBD spot count treated with ACE2-Fc. N ≥ 2000 cells from triplicate wells each from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. (e) Table showing the EC50 values for Ab1, Ab2, and ACE2-Fc based on spot count from (b) and (d). Images were captured using a 40× objective. (f) Illustration of QD608-RBD internalization via receptor-mediated endocytosis and the inhibition using Ab1, Ab2, and ACE2-Fc.
