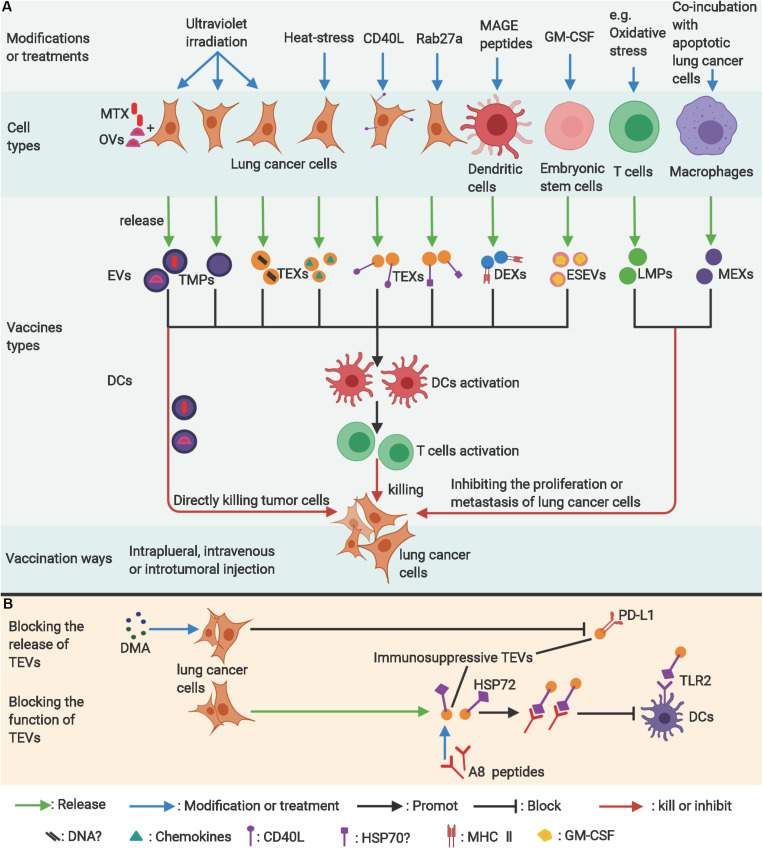
FIGURE 3.
The applications of EVs in lung cancer therapy. (A) Modified lung cancer cells, dendritic cells, or embryonic stem cell–derived extracellular vesicles can be used to stimulate antitumor immunity as vaccines. Modified T-cells or macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles can potentially inhibit proliferation of lung cancer cells. (B) Blocking the release of exosomes from lung cancer cells (TEXs) or neutralizing the immunosuppressive molecules on TEXs are potentially effective antitumor ways. ?, uncertain; MAGE, melanoma antigen gene; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MTX, methotrexate; OVs, Oncolytic virus; TMPs, lung tumor-derived microparticles; TEVs, EVs from lung tumor cells; TEXs, Lung cancer-derived exosomes; DEXs, exosomes from dendritic cells; ESEVs, EVs from embryonic stem cells; LMPs, T-lymphocyte-derived microparticles; MEXs, exosomes derived from macrophages; DMA, Dimethyl amiloride; HSP72, Heat Shock Protein 72; TLR2, toll-like receptor 2. Figure created with BioRender.com.