Figure 1. Mechanisms explaining how Sgo1 regulates centromeric cohesion during mitosis.
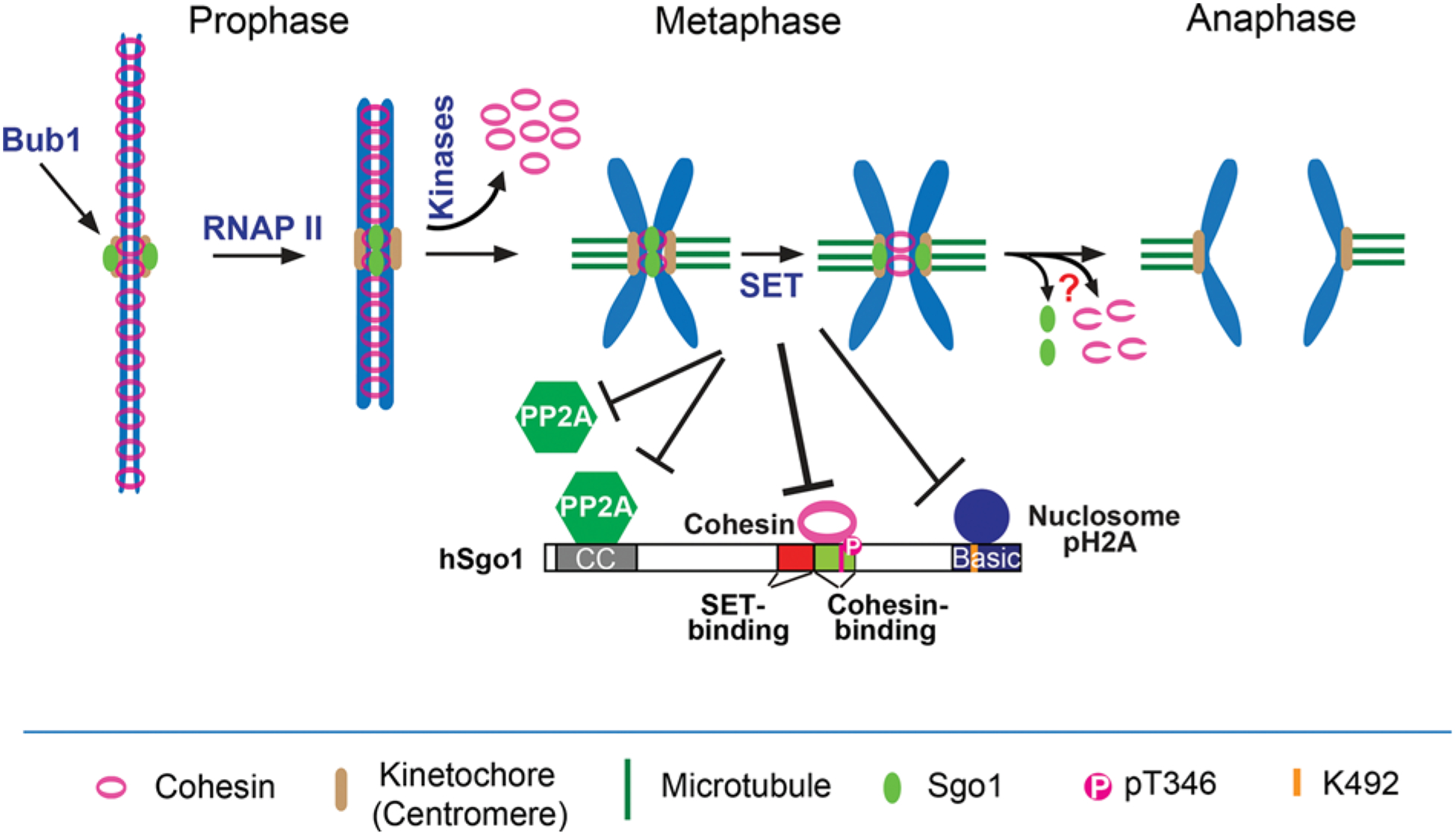
In prophase, Bub1-phosphorylated H2A recruits Sgo1 to kinetochores. RNA Polymerase (RNAP) II transcription promotes the relocation of kinetochore Sgo1 to the inner centromere, where Cdk1-phosphorylated Sgo1 binds to cohesin to protect centromeric cohesion. Cohesin on chromosome arms is released with the aid of multiple mitotic kinases. At metaphase-to-anaphase transition, SET removes Sgo1 from inner centromeres to de-protect centromeric cohesion by disrupting either the Sgo1–cohesin or Sgo1-nuclosome binding or both. SET may also inhibit PP2A activity to de-protect centromeric cohesion. It is unknown whether Separase cleavage of centromeric cohesin requires Sgo1 removal from inner centromeres (marked by “?”).
