Figure 3: Voltage-dependence of activation and inactivation kinetic variables at steady-state.
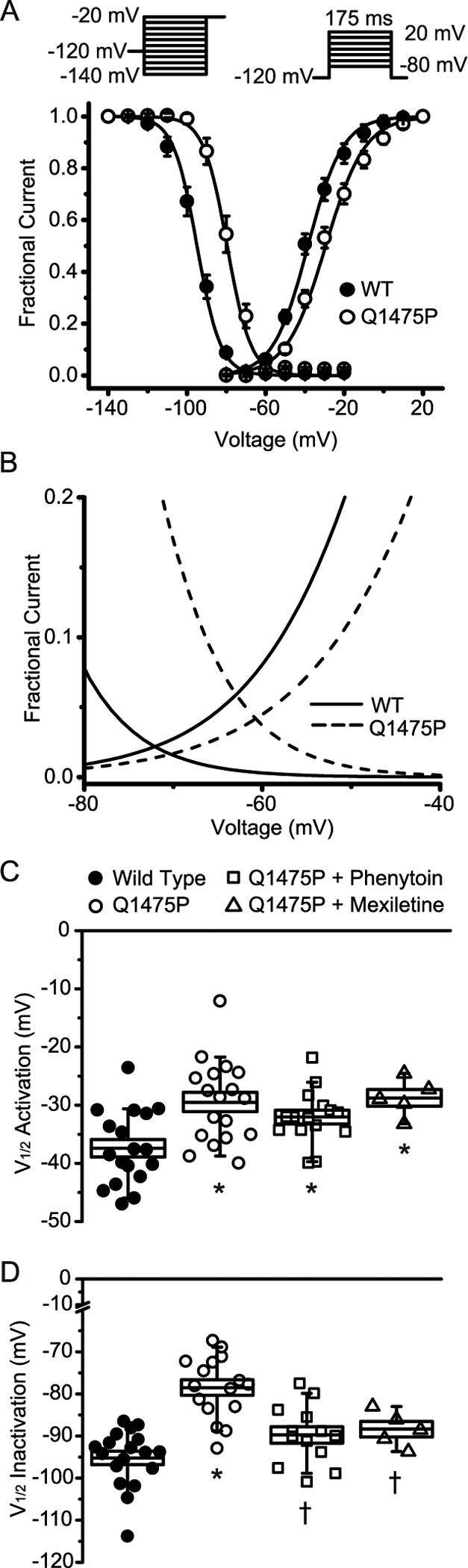
(A) Steady-state activation and inactivation curves for WT and Nav1.5-Q1475P obtained using the voltage protocols depicted as insets. Data points were subjected to curve fitting to a Boltzmann function and the solid lines were derived from the averaged fitted parameters. (B) The steady-state activation and inactivation curves are shown over a limited voltage range to depict the larger “window” current of Nav1.5-Q1475P. (C and D) The voltages of half-maximal (V½) activation and inactivation obtained from the curve fitting are summarized and depicted for the various experimental groups (WT n=18; Q1475P n=16; Q1475P plus phenytoin n=13; Q1475P plus mexiletine n=7). Phenytoin and mexiletine were each applied at 100 μM. *p < 0.05 versus WT; †p < 0.05 drug groups versus Q1475P.
