Fig. 1. MacroH2A1.2 loss impairs female survival and X ploidy.
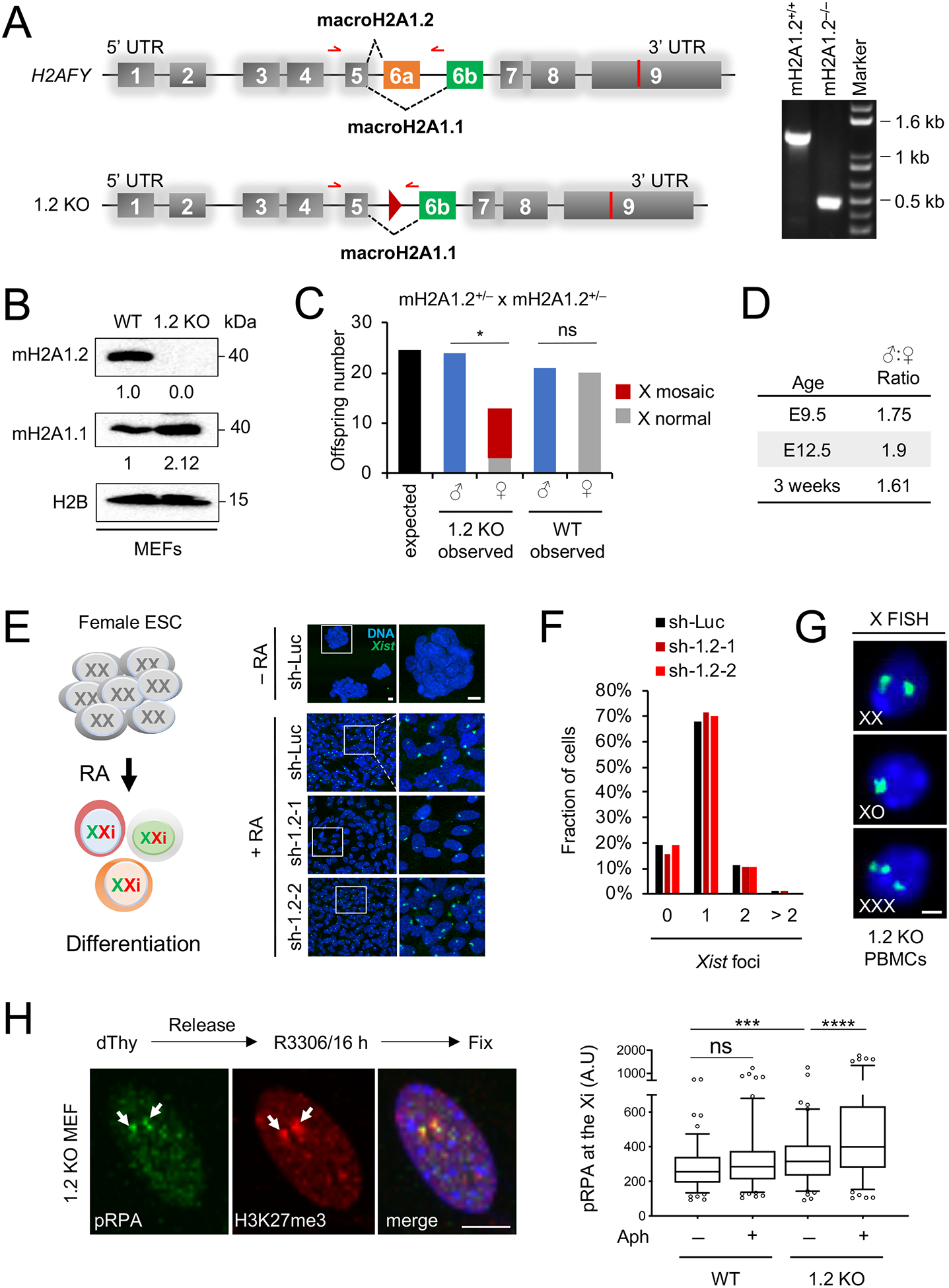
(A) Schematic of the macroH2A1-encoding H2AFY gene and the macroH2A1.2 knockout allele (1.2 KO), not to scale. Exon 6a was deleted by Cre/loxP-mediated recombination, resulting in a residual loxP site (triangle). Alternative splicing resulting in macroH2A1.1 or macroH2A1.2 is indicated. Red arrows depict primers used for PCR genotyping, resulting in a 1.3 kb fragment for the WT allele and 0.5 kb for the 1.2 KO allele. A representative PCR for the indicated genotypes is shown. (B) Western blot for macroH2A1 variants in MEFs from WT and 1.2 KO littermates. (C) Number of WT and 1.2 KO males and females at time of weaning, based on 28 litters from macroH2A1.2+/− parents. X-mosaicism was determined as in (G) for all female KO offspring, and for a subset of male KO and female WT offspring, see Fig S1O. * p = 0.01, based on a two-tailed binomial test, ns: not significant. (D) Male:Female ratio in 1.2 KO mice analyzed at the indicated ages, twoway comparisons between each of the three age groups revealed no significant differences based on Fisher’s exact test. (E) Xist induction in differentiating female mouse ES cells expressing a control shRNA (sh-Luc, n = 218 cells) or one of two distinct shRNAs against macroH2A1.2, sh-1.2–1 (n = 260 cells) and sh-1.2–2 (n = 379 cells), see Table S2 for shRNA sequences. A schematic for retinoic-acid induced ES cell differentiation is shown. Xist was detected by RNA FISH, nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342, representative images and enlarged inlays are shown, scale bars: 10 μm. (F) Fraction of cells with the indicated number of Xist foci, based on (E). (G) X-chromosome FISH in PBMCs from 1.2 KO mice. Female cells with X counts other than XX were considered X-mosaic, scale bar: 10 μm. (H) Representative IF images and quantification showing pRPA localization to the Xi. H3K27me3 is used to mark the Xi (white arrows). A minimum of 100 cells were analyzed per group. scale bar: 10 μm. *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, based on Mann-Whitney U test. See also Fig. S1, Table S2.
