Fig. 3. Treatment with L-Moses inhibits TgGCN5b bromodomain binding activity in vitro.
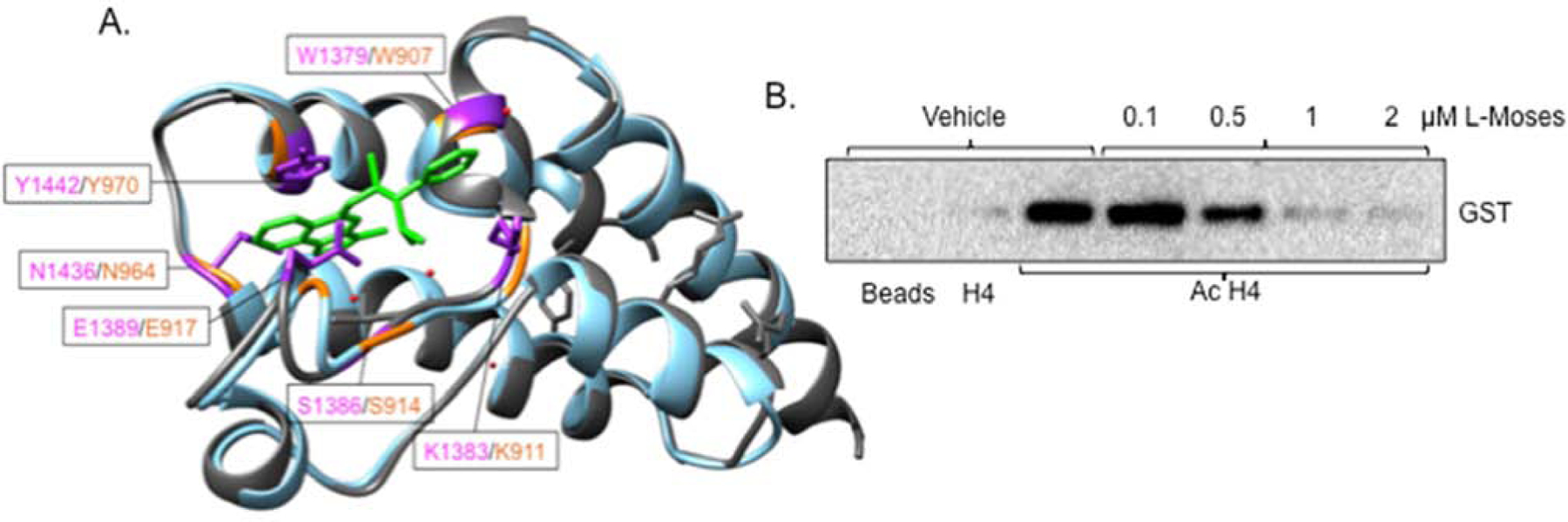
(A) Predicted model of TgGCN5b bromodomain (blue) superimposed with the PfGCN5 bromodomain (grey) bound to L-Moses (green) (PDB identification of PfGCN5 complexed to L-Moses is 5tpx) using Chimera Matchmaker. Purple residues are those in P. falciparum that interact with L-Moses. Orange text represents the corresponding residues in Toxoplasma. Red dots represent water molecules. (B) BRD binding assay. Western blot was probed with anti-GST to display recombinant, GST-tagged GCN5b bromodomain binding to H4 or acetylated H4 (AcH4) in the presence of vehicle or L-Moses.
