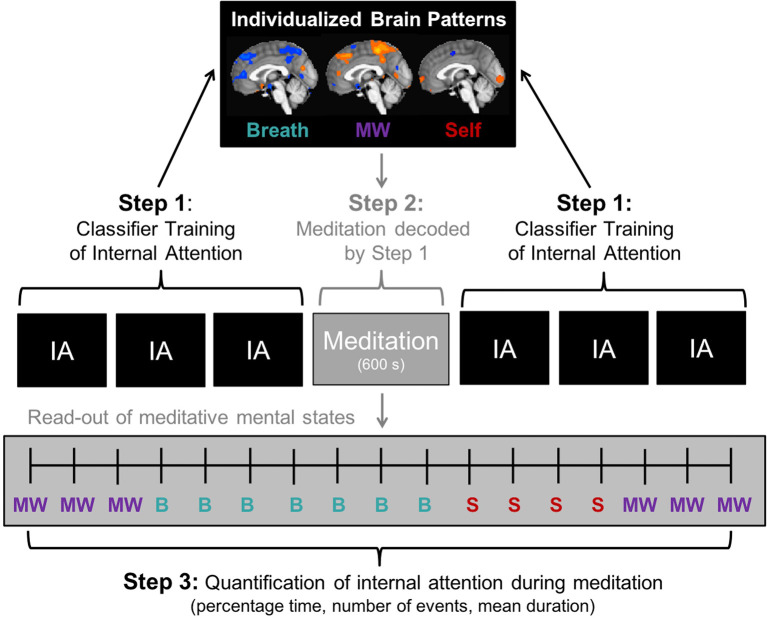
Figure 1.
EMBODY Framework: Evaluating Multivariate Maps of Body Awareness to measure internal attention (IA) states during meditation. Step 1. Brain pattern classifier training. Machine learning algorithms are trained in fMRI neural patterns associated with internal mental states in the IA task. IA is directed via auditory instructions to pay attention with eyes closed to the breath, mind wandering (MW) self-referential processing (Self), and control conditions of attention to the feet and ambient sounds (see Figure 2). Individualized brain patterns for each participant are learned using n-1 cross-validation with six blocks of the IA task (volume N = 2,160). Step 2. Meditation period classification. Neural patterns are collected during a 10-min meditation period (in this case, focused attention to the breath; administered in the middle of six IA blocks), and are decoded by multi-voxel pattern analysis (MVPA) using the unique brain patterns learned in Step 1. Meditation is decoded second-by-second into mental states of attention to breath (B), MW, or self-referential processing (S), producing an estimate of distinct and fluctuating mental states during meditation. Step 3. Quantification of internal attention during meditation. From the temporal read-out of meditative mental states in Step 2, attention metrics during meditation can be quantified and estimated including percentage time spent in each mental state, the number of times engaged in each mental state (“events”), and mean duration spent in each mental state.